
|
|
GLOBALIZATION: The generalized expansion of international economic activity which includes increased international trade, growth of international investment (foreign investment) and international migration, and increased proliferation of technology among countries. Globalization is the increasing world-wide integration of markets for goods, services, labor, and capital. It is an ongoing process that started several centuries ago. However, most people would agree that today we are in a period of rapid globalization as international economic activity has accelerated in the last 200 years or so.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
|
Lesson 10: Utility and Demand | Unit 4: On To Demand
|
Page: 14 of 21
|
|
Topic:
A Generalized Choice
|
|
|
|
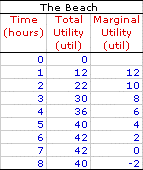
- In many cases buyers are making choices between ONE good and EVERY other good that they could be purchasing.
- The presumption is that every other good satisfies the rule of consumer equilibrium.
- The question now becomes: How much beach frolicking do I undertake (or purchase) given that my going marginal utility-price ratio is 3 utils per dollar for other goods?
- Employing the rule of consumer equilibrium, I need to equate the marginal utility-price ratio (MU/P) for beach frolicking with the marginal utility-price ratio for other goods.
MU/P for beach frolicking = MU/P for other goods - Because the marginal utility-price ratio for other goods is 2 utils per dollar, the time I spend at the beach needs generates to generate the same 2 utils per dollar.
- If the price per hour at the beach is $2, then I need to stay at the beach until my marginal is 4 utils, a value generated at 5 hours. This gives me a marginal utility-price ratio (MU/P) for beach activity of 2 utils per dollar.
- I have satisfied the rule of consumer equilibrium!
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
AGGREGATE SUPPLY DETERMINANTS An assortment of ceteris paribus factors that affect short-run and long-run aggregate supply, but which are assumed constant when the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves are constructed. Changes in any of the aggregate supply determinants cause the short-run and/or long-run aggregate supply curves to shift. While a wide variety of specific ceteris paribus factors can cause the aggregate supply curves to shift, they are commonly grouped into three broad categories--resource quantity, resource quality, and resource price.
Complete Entry | Visit the WEB*pedia |



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time strolling through a department store looking to buy either a coffee cup commemorating the first day of winter or a video game player. Be on the lookout for neighborhood pets, especially belligerent parrots.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The portrait on the quarter is a more accurate likeness of George Washington than that on the dollar bill.
|

|
|
"The past is a foreign country; they do things differently there." -- Leslie Poles Hartley, Writer
|

|
ECU
European Currency Unit
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


