
|
|
DECLINE STAGE: The final stage of the product life cycle, characterized by a drastic drop off in profits. A company needs to decide how long to continue to support a product during this stage. Advertising and promotion can help maintain sales for a period of time. Ultimately, the cost-benefit tradeoff forces the business to discontinue the manufacturing of a product in this stage. Sometimes this happens quite rapidly and in some cases the product continues in this stage for many years.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           FACTOR DEMAND CURVE: A graphical representation of the relationship between the price to a factor of production and quantity of the factor demanded, holding all ceteris paribus factor demand determinants constant. The factor demand curve is one half of the factor market. The other half is the factor supply curve. The factor demand curve indicates the quantity of a factor demanded at alternative factor prices. While all factors of production, or scarce resources, including labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship, have factor demand curves, labor is the factor most often analyzed. Like other demand curves, the factor demand curve is generally negatively sloped. Higher factor prices are associated with smaller quantities demanded and lower factor prices go with larger quantities demanded.For a firm that hires factors in a perfectly competitive market, factor demand curve is essentially the marginal revenue product curve. Monopsony and other imperfectly competitive firms with some degree of market control over the factor market do not have a clear-cut factor demand curve. In other words, factor price and quantity demanded may or may not be inversely related. | Factor Demand Curve | 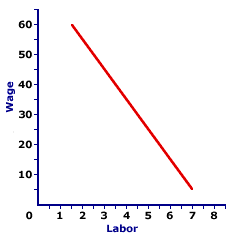 |
The exhibit to the right displays a typical factor demand curve. This particular curve is the demand for labor by Waldo's TexMex Taco World, a hypothetical Shady Valley restaurant specializing in the production of Super Deluxe TexMex Gargantuan Tacos (with sour cream and jalapeno peppers).The number of workers is measured on the horizontal axis and the wage paid per worker is measured on the vertical axis. This factor demand curve indicates that Waldo is willing to hire 4 workers at $35 each, 5 workers at $25 each, and 6 workers at $15 each. The wage declines with an increase in the number of workers employed, because extra workers contribute less and less to total production and to total revenue. The most important feature of this factor demand curve is the negative slope. Waldo's TexMex Taco World is willing and able to pay workers a higher wage if they employ fewer workers. However, if they employ more workers, then they are willing and able to pay a lower wage. The primary reason for this inverse relation between wage and quantity demanded is the productivity of the workers and the law of diminishing marginal returns. As Waldo's TexMex Taco World employs more workers IN A GIVEN RESTAURANT, marginal product declines, each additional worker contributes less to total product as the law of diminishing marginal returns kicks in. However, with less production to sell, Waldo's TexMex Taco World generates less revenue. In other words, the law of diminishing marginal returns causes a decline in marginal physical product, and consequently a decline in marginal revenue product. But if workers generate less revenue, then Waldo's TexMex Taco World is willing and able to pay a lower wage. Because the factor demand curve, like other curves, is constructed to reflect the relationship between two variables, factor price and factor quantity demanded, changes in other variables cause the curve to shift. The three most noted curve-shifting factor demand determinants are product price, factor productivity, and prices of other factors.

Recommended Citation:FACTOR DEMAND CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
RED AGGRESSERINE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a flea market wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from long-lost relatives.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The penny is the only coin minted by the U.S. government in which the "face" on the head looks to the right. All others face left.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
IAB
Inter-American Bank
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


