
|
|
OLIGOPOLY AND MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION: Oligopoly and monopolistic competition have some similarities, but also have a few important differences. Both are examples of imperfect competition on the market structure continuum between ideals of perfect competition and monopoly. However, oligopoly contains a small number of large firms and monopolistic competition contains a large number of small firms. The dividing line between oligopoly and monopolistic competition can be blurred due to the number of firms in the industry.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           LOSS MINIMIZATION RULE: A rule stating that a firm minimizes economic loss by producing output in the short run that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost if price is less than average total cost but greater than average variable cost. This is one of three short-run production alternatives facing a firm. The other two are profit maximization (if price exceeds average total cost) and shutdown (if price is less than average variable cost). | Production Alternatives | | Price and Cost | Result |
|---|
| P > ATC | Profit Maximization | | ATC > P > AVC | Loss Minimization | | P < AVC | Shutdown |
The loss minimization rule applies to a firm that is incurring a short-run economic loss that is less than total fixed cost. This occurs if the price received is less than average total cost, but greater than average variable cost. It is not an absolute rule so much as it is an alternative that any profit maximizing firm is inclined to pursue given production cost and market conditions.Loss minimization is one of three short-run production alternatives facing a firm. All three are displayed in the table presented here. The other two are profit maximization and shutdown. - With profit maximization, price exceeds average total cost at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost. In this case, the firm generates an economic profit.
- With shutdown, price is less than average variable cost at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost. In this case, the firm incurs a smaller loss by producing no output and incurring a loss equal to total fixed cost.
In the short run, a firm incurs total fixed cost whether or not it produces any output. As such, if the market price falls below average total cost, it must decide if the economic loss from producing the quantity of output that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost is more or less than the economic loss incurred with shutting down production in the short run (which is equal to total fixed cost).| Incurring a Loss | 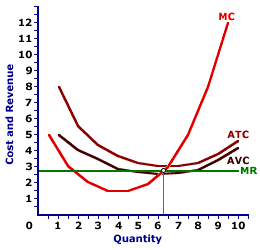 |
The key criterion for this decision is price relative to average variable cost. - If price is greater than average variable cost, a firm receives sufficient revenue to pay ALL variable cost plus some fixed cost. As such, the economic loss is less than total fixed cost. A firm is better off producing the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost than producing no output, receiving no revenue, and incurring a loss equal to total fixed cost.
- If price is less than average variable cost, a firm does not receive enough revenue to pay variable cost let alone any part of fixed cost. As such, the economic loss of operating is greater than total fixed cost. A firm is better off shutting down production in the short run, producing zero output, and awaiting a higher price.
The exhibit here illustrates the loss minimizing situation that exists for a hypothetical perfectly competitive firm, Phil the zucchini-growing gardener. The going market price (marginal revenue) of $2.60 per pound of zucchinis received by Phil intersects the marginal cost curve between the average total cost curve and the average variable cost curve.Because price falls short of average total cost, Phil incurs a loss. However, because price exceeds average variable cost, Phil incurs a smaller loss by producing 6.25 pounds of zucchinis than by shutting down production.

Recommended Citation:LOSS MINIMIZATION RULE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads seeking to buy either an extra large beach blanket or a large flower pot shaped like a Greek urn. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Francis Bacon (1561-1626), a champion of the scientific method, died when he caught a severe cold while attempting to preserve a chicken by filling it with snow.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
OPBU
Operating Budget
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


