
|
|
HIERARCHY OF NEEDS: Developed by Abraham Maslow, the notion that people are motivated to satisfy basic physiological needs (food, shelter, etc.) before moving on to satisfying higher psychological needs (security, companionship, etc.). These alternative needs are layered in a hierarchial pattern with physiological needs on the bottom, safety needs on the second layer, belonging needs on the third layer, esteem needs on the fourth layer, and self-actualization needs at the top. This hierarchy of needs has been used to help explain the progress of human societies from agrarian to manufacturing to service to information.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MONOPOLY PROFIT: Economic profit generated as a result of a firm's market control. It is termed monopoly profit as a reflection of the most prominent market structure with market control--monopoly. However, any market structure with market control, including oligopoly and monopolistic competition, can generate monopoly profit. The existence of monopoly profit is an indication that a firm is NOT efficiently allocating resources. While market control in no way guarantees that a firm receives monopoly profit, there is no way to obtain monopoly profit WITHOUT market control. Monopoly profit arises when a firm with market control is able to set a price that exceeds average total cost. This is termed monopoly profit in honor of the monopoly market structure with the greatest market control and the one most likely to generate monopoly profit.Market control enables a firm to acquire monopoly profit for two key reasons. - One, a firm that faces a negatively-sloped demand curve charges a higher price than a comparable perfectly competitive firm with no market control. The higher the price, the more likely it is to exceed average cost and thus to generate economic profit.
- Two, barriers to entry are one source of market control, especially for monopoly. Such barriers prevent new firms from entering the market in response to above-normal economic profit. Economic or monopoly profit is not eaten away by competition.
| Monopoly Profit | 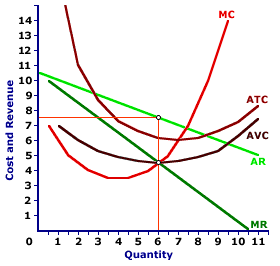 |
Consider the production and sale of Amblathan-Plus, the only cure for the deadly (but hypothetical) foot ailment known as amblathanitis. This drug is produced by the noted monopoly firm, Feet-First Pharmaceutical.A typical profit-maximizing output determination using the marginal revenue and marginal cost approach is presented in this exhibit. Feet-First Pharmaceutical maximizes profit by producing output that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost, which is 6 ounces of Amblathan-Plus in this example. The corresponding price charged is $7.50. Because price is greater than average cost, Feet-First Pharmaceutical receives an economic profit, which by virtue of its monopoly market structure is monopoly profit. To highlight this profit, click the [Monopoly Profit] button. The yellow rectangle, representing the difference between total cost and total revenue, is the monopoly profit received by Feet-First Pharmaceutical. This profit is determined in the following way: - First, the total revenue received by Feet-First Pharmaceutical is equal to the $7.50 price times the 6 ounces of Amblathan-Plus sold, which is $45 (= 6 x $7.50).
- Second, the total cost incurred by Feet-First Pharmaceutical is equal to the $6.17 average total cost times the 6 ounces of Amblathan-Plus sold, which is $37 (= 6 x $6.17).
- Third, monopoly profit is the difference between total revenue and total cost, which is $8 = ($45 - $37).
Not only is Feet-First Pharmaceutical more likely to generate such monopoly profit, but entry barriers (an exclusive patent on the production of Amblathan-Plus) prevents other firms from entering this market.

Recommended Citation:MONOPOLY PROFIT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
RED AGGRESSERINE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a flea market wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from long-lost relatives.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
North Carolina supplied all the domestic gold coined for currency by the U.S. Mint in Philadelphia until 1828.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
TNV
Total Net Value
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


