
|
|
SCARCITY: A pervasive condition of human existence that exists because society has unlimited wants and needs, but limited resources used for their satisfaction. In other words, while we all want a bunch of stuff, we can't have everything that we want. In slightly different words, this scarcity problem means: (1) that there's never enough resources to produce everything that everyone would like produced; (2) that some people will have to do without some of the stuff that they want or need; (3) that doing one thing, producing one good, performing one activity, forces society to give up something else; and (4) that the same resources can not be used to produce two different goods at the same time. We live in a big, bad world of scarcity. This big, bad world of scarcity is what the study of economics is all about. That's why we usually subtitle scarcity: THE ECONOMIC PROBLEM.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
|
Lesson 8: Market Shocks | Unit 3: Single Shifts
|
Page: 8 of 20
|
|
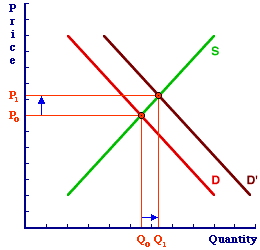
An increase in demand caused by one of the demand determinants.- Initial equilibrium market at price Po and quantity Qo
- Buyers acquire a sudden "appetite" for hot fudge sundaes.
A summary: - The demand curve shifts rightward.
- The initial equilibrium is no longer an equilibrium.
- The new equilibrium is at the intersection of the original supply curve with the new demand curve.
- New equilibrium price is P1 and new equilibrium quantity is Q1.
The six steps of market adjustment for an increase in demand:- A determinant changes. We have a greater appetite for hot fudge sundaes.
- A curve to shifts. The demand curve for hot fudge sundaes shifts rightward.
- A shortage or a surplus occurs. The increase in demand causes a shortage of hot fudge sundaes.
- The price changes. The price of hot fudge sundaes goes up.
- The quantities demanded and supplied change. The quantity supplied for hot fudge sundaes increases while their quantity demand is reduced.
- The market imbalance is eliminated and equilibrium is restored. The shortage of hot fudge sundaes is eliminated. The price is higher and the quantity exchanged is more.
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
GOVERNMENT CONSUMPTION EXPENDITURES AND GROSS INVESTMENT The official item in the National Income and Product Accounts maintained by the Bureau of Economics Analysis measuring government purchases undertaken by the government sector. Government consumption expenditures and gross investment averages between 15-20 percent of gross domestic product. As might be expected, this percentage tends to be ebb and flow with the political winds. Some political leaders prefer more government activity, others less. However, this percentage is even more dependent on military conflicts and wars that require massive government activity. The other official expenditures included in the National Income and Product Accounts are personal consumption expenditures, gross private domestic investment, and net exports of goods and services.
Complete Entry | Visit the WEB*pedia |



|

|
PURPLE SMARPHIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time looking for a downtown retail store hoping to buy either a Boston Red Sox baseball cap or a square lamp shade with frills along the bottom. Be on the lookout for mail order catalogs with hidden messages.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Okun's Law posits that the unemployment rate increases by 1% for every 2% gap between real GDP and full-employment real GDP.
|

|
|
"It is not because things are difficult that we do not dare; it is because we do not dare that they are difficult. " -- Seneca, statesman, dramatist, philosopher
|

|
CAPM
Capital Asset Pricing Model
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


