
|
|
OMO: The abbreviation for open market operations, which is the Federal Reserve System's buying and selling of government securities in an effort to alter bank reserves and subsequently the nation's money supply. These actions, under the direction of the Federal Open Market Committee, are the Fed's number one, most effective, most often used tool of monetary policy. If, for example, the Fed wants to increase the money supply (termed easy money) it buy's government securities. If the Fed chooses to reduce the money supply (called tight money) it sells some government securities.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
|
Lesson 4: Production Possibilities | Unit 5: Investment
|
Page: 19 of 24
|
|
Investment is the tradeoff between consumption goods used for current satisfaction and capital goods that expand future productive capabilities.- Investment is not just putting money into the stock market. Investment is giving up current satisfaction to obtain greater future production, usually seen as giving up consumption goods to produce capital goods.
- Education and human capital that increase the productive skills and ability of labor.
- Exploration for mineral or fossil fuel deposits that add to land resources.
- Scientific research that expands technology and resource quality.
- The downside of investment is risk. There is no guarantee that you'll get something tomorrow.
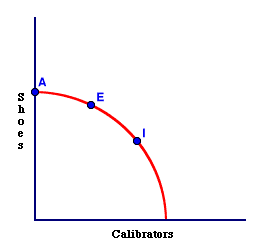
Let's consider this basic tradeoff between capital and consumption.- Capital and consumption are the two basic types of goods needed for investment. If we produce more calibrators (capital), then we give up some jogging shoes (consumption).
- This tradeoff IS the fundamental act of investment. In the graph to the right, if we move from bundle A to E to I, we are giving up jogging shoes and getting calibrators.
We are investing!
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
GOOD TYPES The economy produces four distinct types of goods based on two key characteristics -- consumption rivalry and nonpayer excludability. Consumption rivalry arises if consumption of a good by one person prevents another from also consuming. Nonpayer excludability means potential consumers who do not pay for a good can be excluded from consuming. Private goods are rival in consumption and easily subject to the exclusion of nonpayers. Public goods are nonrival in consumption and the exclusion of nonpayers is virtually impossible. Near-public goods are nonrival in consumption and easily subject to exclusion. Common-property goods are rival in consumption and not easily subject to exclusion. Private goods can be efficiently exchanged through markets. Public, near-public and common-property goods cannot, but require some degree of government involvement for efficiency.
Complete Entry | Visit the WEB*pedia |



|

|
YELLOW CHIPPEROON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time flipping through mail order catalogs looking to buy either income tax software or a how-to book on the art of negotiation. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
There were no banks in colonial America before the U.S. Revolutionary War. Anyone seeking a loan did so from another individual.
|

|
|
"I learned about the strength you can get from a close family life. I learned to keep going, even in bad times. I learned not to despair, even when my world was falling apart. I learned that there are no free lunches. And I learned the value of hard work. " -- Lee Iacocca
|

|
ABE
Association of Business Executives
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


