
|
|
IEBNR: The abbreviation for income earned but not received. The three types of income earned but not received by the factors of production are Social Security taxes, corporate profits taxes, and undistributed corporate profits. In each case a factor of production has rightfully "earned" the income by contributing to valuable production contained in gross domestic product. However, because this income is not paid to the factor and it is not income received by the household sector. IEBNR is subtracted from national income to calculate personal income.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           IMPORTS LINE: A graphical depiction of the relation between imports bought from the foreign sector and the domestic economy's aggregate level of income or production. This relation is most important for deriving the net exports line, which plays a minor, but growing role in the study of Keynesian economics. An imports line is characterized by vertical intercept, which indicates autonomous imports, and slope, which is the marginal propensity to import and indicates induced imports. The aggregate expenditures line used in Keynesian economics is derived by adding or stacking the net exports line, derived as the difference between the exports line and imports line, onto the consumption line, after adding investment expenditures and government purchases. The imports line shows the relation between imports purchased from the foreign sector and aggregate income or production. The income and production measures most commonly used are national income and gross domestic product. The purpose of the imports line is to graphically illustrate the imports-income relation for the foreign sector, which is then used to derive the net exports line by vertically subtracting it from the exports line, after which it is then integrated into the aggregate expenditures line used in Keynesian economics.Net exports are the difference between exports and imports, or exports minus imports. Exports are purchases of domestic production by the foreign sector and imports are purchases of foreign production by the domestic economy. While exports are totally autonomous, imports are induced by the level of domestic income and production. Reflecting this, the imports line is positively-sloped, with the slope equal to the marginal propensity to import (MPM). The vertical intercept, or Y-intercept, of the imports line is then autonomous imports. | Imports Line | 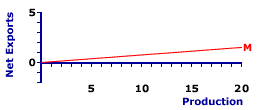 |
The positively-sloped red line, labeled M in the exhibit to the right, indicates a typical imports line. Line any straight line, this imports line is characterized by two key parameters, intercept and slope. The intercept indicates autonomous imports and the slope indicates induced imports.Identifying numbers for these two parameters for this particular line indicates that the intercept is $0, meaning autonomous imports is $0, and the slope is 0.075, meaning a $1 increase in domestic income or production induces a $0.075 increase in imports. In this particular case, the imports line has a zero intercept, indicating no autonomous imports, but that need not be the case. Most notable is that the slope of the imports line is the marginal propensity to import (MPM).

Recommended Citation:IMPORTS LINE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads seeking to buy either an extra large beach blanket or a large flower pot shaped like a Greek urn. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The portion of aggregate output U.S. citizens pay in taxes (30%) is less than the other six leading industrialized nations -- Britain, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, or Japan.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
ES
Singapore Stock Exchange
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


