
|
|
WILDCAT STRIKE: An unofficial and usually spontaneous strike or work stoppage by union members. A wildcat strike is not authorized by the labor union representing the workers. Such strikes generally occur because (1) labor has specific problems or concerns that have not been satisfactorily addressed by employers or (2) workers feel that union leaders are not acting in the best interest of the union members. This is also termed an outlaw strike.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           RECESSIONARY GAP: The difference between the equilibrium real production achieved in the short-run aggregate market and full-employment real production that occurs when short-run equilibrium real production is less than full-employment real production. A recessionary gap, also termed a contractionary gap, is associated with a business-cycle contraction. This is one of two alternative output gaps that can occur when short-run equilibrium generates production that differs from full employment. The other is an inflationary gap. A recessionary gap is central to the study of macroeconomics, especially the analysis of business cycles and the problem of unemployment that perpetually puzzles political leaders. Unemployment is the prime problem of a business-cycle contraction which corresponds to a recessionary gap in the aggregate market.| Recessionary Gap | 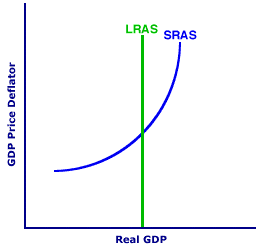 |
The aggregate market presented in the graph to the right can provide an understanding of a recessionary gap. The vertical long-run aggregate supply curve, labeled LRAS, marks full-employment real production. Long-run equilibrium in the aggregate market necessarily results in full-employment real production.The positively-sloped short-run aggregate supply curve is labeled SRAS. Short-run equilibrium in the aggregate market occurs at the price level and real production corresponding to the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and this SRAS curve. Should short-run real production fall short of full-employment real production, then a recessionary gap results. However, to identify a recessionary gap an aggregate demand curve needs to be added to the graph. To include the aggregate demand curve and illustrate a recessionary gap for this aggregate market, click the [Recessionary Gap] button. Doing so reveals a short-run equilibrium level of real production that is less than full employment, which is a recessionary situation. Note that the aggregate demand curve, labeled AD, intersects the SRAS curve at a real production level to the left of the LRAS curve. This means the short-run real production is less than full-employment real production. The difference between short-run equilibrium real production and full-employment real production is the recessionary gap. The basic reason for the emergence of a recessionary gap is short-run resource price rigidity. Because resource prices, especially wages, tend to be inflexible in the short-run, any downturn in the economy (that is, decline in aggregate demand) generates less production and employment, and thus higher unemployment, rather than lower wages and resource prices. The primary problem associated with a recessionary gap is unemployment. This is not only detrimental to the unemployed resources, who suffer personal hardships, but it also means less real production is available to the rest of the economy. Because of this undesirability, government often considers alternative stabilization policies to correct the situation, including expansionary monetary and fiscal policies. The intent of such policies is to increase the short-run real production level to the long-run full-employment level of real production. A recessionary gap also sets in motion the self-correction adjustment mechanism of the aggregate market. Resource market imbalances, in this case surpluses that generate unemployment, trigger resource price decreases that cause the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift rightward. This shift also increases short-run real production and moves it toward the full-employment level of real production.

Recommended Citation:RECESSIONARY GAP, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads seeking to buy either an extra large beach blanket or a large flower pot shaped like a Greek urn. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Before 1933, the U.S. dime was legal as payment only in transactions of $10 or less.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
ATM
Automated Teller Machine
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


