
|
|
PERFECT COMPETITION, REVENUE DIVISION: The marginal approach to analyzing a perfectly competitive firm's short-run profit maximizing production decision can be used to identify the division of total revenue among variable cost, fixed cost, and economic profit. The U-shaped cost curves used in this analysis provide all of the information needed on the cost side of the firm's decision. The demand curve facing the firm (which is also the firm's average revenue and marginal revenue curves) provides all of the information needed on the revenue side.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           SELF CORRECTION, RECESSIONARY GAP: The automatic process in which the aggregate market eliminates a recessionary gap created by a short-run equilibrium that is less than full employment through decreases in wages (and other resource prices). The self-correction mechanism is triggered by short-run resource market imbalances that are closed by long-run price flexibility. The self-correction process of the aggregate market also acts to close an inflationary gap with higher wages (and other resource prices). Self correction is seen as shifts of the short-run aggregate supply curve caused by changes in wages and other resource prices. The self-correction mechanism acts to close a recessionary gap with lower wages and an increase in the short-run aggregate supply curve.With a recessionary gap, short-run equilibrium real production is less than full-employment real production, meaning resource markets have surpluses. In particular, labor unemployment exceeds the natural rate. Self correction is the process in which these temporary imbalances are eliminated through flexible prices as the aggregate market achieves long-run equilibrium. The key to this process is that changes in wages and other resource prices cause the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift. | Closing A Recessionary Gap | 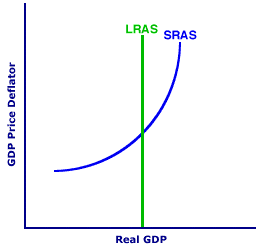 |
The self-correction closure of a recessionary gap in the aggregate market can be illustrated using the exhibit to the right. The vertical axis measures the price level (GDP price deflator) and the horizontal axis measures real production (real GDP). This graph presents the two aggregate supply curves--long run and short run--but no aggregate demand curve. The vertical curve labeled LRAS is the long-run aggregate supply curve which marks full-employment real production. The positively-sloped curve labeled SRAS is then the short-run aggregate supply curve. The positioning of the aggregate demand curve and the point of intersection with the short-run aggregate supply curve indicates the recessionary gap. - Recessionary Gap: Click the [Recessionary Gap] button to reveal this output gap. With a recessionary gap, short-run equilibrium real production is less than full-employment real production, meaning resource markets have surpluses, and in particular labor is unemployed.
- Closing the Gap: In the long-run, this recessionary gap is closed with lower wages and an increase in short-run aggregate supply. To illustrate this result, click the [Lower Wages] button. This button-clicking shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right. A new equilibrium is achieved by the intersection of the new SRAS curve and the original AD curve. This intersection also coincides with the LRAS curve.
In the long run, wages and resource prices are flexible and they decline enough to eliminate imbalances in the resource markets. The result of declining wages (and other resource prices) is a reduction in production cost. A decrease in production cost causes an increase in short-run aggregate supply, or a rightward shift of the SRAS curve.Note that the SRAS curve shifts rightward until it intersects BOTH the LRAS and AD curves at full-employment real production, which is long-run equilibrium. In particular, the new long-run equilibrium is at the full-employment level of real production. The SRAS curve absolutely MUST shift until this long-run equilibrium is reached. If the aggregate market does NOT reach long-run equilibrium, resource market imbalances persist, resource prices and production cost decline further, and the SRAS curve shifts more. However, once long-run equilibrium is reached, resource market imbalances are eliminated, resource prices and production cost do not change, and the SRAS curve does not shift any further.

Recommended Citation:SELF CORRECTION, RECESSIONARY GAP, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 1, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time waiting for visits from door-to-door solicitors looking to buy either a coffee cup commemorating the first day of winter or a video game player. Be on the lookout for malfunctioning pocket calculators.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, almost 2 million children were employed as factory workers.
|

|
|
"Experience keeps a dear school, but fools will learn in no other. " -- Benjamin Franklin
|

|
GMB
Good Merchandise Brand
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


