
|
|
LAW OF SUPPLY: The direct relationship between supply price and the quantity supplied, ceteris paribus. This fundamental economic principle indicates that as the price of a commodity increases, then the quantity of the commodity that sellers are able and willing to sell in a given period of time, if other factors are held constant, also increases. This law, while not quite as iron-clad as the law of demand, is quite important to the study of markets.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           AVERAGE PRODUCT AND MARGINAL PRODUCT: A mathematical connection between average product and marginal product stating that the change in the average product depends on a comparison between the average product and marginal product. If marginal product is less than average product, then average product declines. If marginal product is greater than average product, then average product rises. If marginal product is equal to average product, then average product does not change. The relation between average product and marginal product is one of several that reflect the general relation between a marginal and the corresponding average. The general relation is this:- If the marginal is less than the average, then the average declines.
- If the marginal is greater than the average, then the average rises.
- If the marginal is equal to the average, then the average does not change.
This general relation surfaces throughout the study of economics. It also applies to average and marginal cost, average and marginal revenue, average and marginal propensity to consume, and well, any other average and marginal encountered in economics.Making Tacos| Average and Marginal Product | 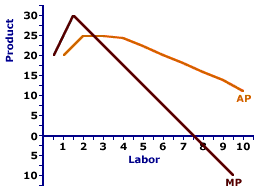 |
The graph at the right for the hourly production of Super Deluxe TexMex Gargantuan Tacos (with sour cream and jalapeno peppers) illustrates the relation between average product and marginal product.The Law of Diminishing Marginal ReturnsThis average-marginal relation for production is closely tied to the law of diminishing marginal returns. Marginal product declines with the onset of diminishing marginal returns. The "hump shape" of the marginal product curve reflects first increasing marginal returns then decreasing marginal returns.For this reason, the "hump shape" of the average product curve is attributable, indirectly, to the law of diminishing marginal returns and the "hump shape" of the marginal product curve. Increasing marginal returns means marginal product is rising and because average product necessarily starts at zero (zero production means zero average product), marginal product lies above average product and causes it to rise, as well. With the onset of decreasing marginal returns, marginal product declines. However, for this initial part of the marginal product decline, average product continues rising because marginal product is still greater. After marginal product falls enough to meet up and intersect average product, average product peaks. As marginal product, again guided by the law of diminishing marginal returns, continues to decline and falls below average product. This causes the decline of average product. In essence, the average product curve plays catch-up to the marginal product curve, sort of follow the leader. At first, marginal product rises, so average product tags along like an annoying younger sibling. Then marginal product decides to fall, so average product chases after it. Because marginal product is guided by the law of diminishing marginal returns, so too is average product.

Recommended Citation:AVERAGE PRODUCT AND MARGINAL PRODUCT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
|
Woodrow Wilson's portrait adorned the $100,000 bill that was removed from circulation in 1929. Woodrow Wilson was removed from circulation in 1924.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
TIFFE
Tokyo International Financial Futures Exchange (Japan)
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


