
|
|
X-INEFFICIENCY: Cost that is higher than it needs to be because a firm is operating inefficiently. This is most often seen for firms that have a great deal of market control, especially monopoly. The lack of competition allows a business to pad it's expenses, hire unneeded employees (like relatives), goof off instead of working, and all sorts of other things that lessen production and increase cost. The business is not penalized for these actions, because market control allows the company to extract whatever price is needed to cover cost.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL PRODUCT AND MARGINAL PRODUCT: A mathematical connection between marginal product and total product stating that marginal product IS the slope of the total product curve. If the total product curve has a positive slope (that is, is upward sloping), then marginal product is positive. If the total product curve has a negative slope (downward sloping), then marginal product is negative. If the total product curve has a zero slope (horizontal), then marginal product is zero. The relation between total product and marginal product is one of several that reflect the general relation between a total and the corresponding marginal. There general relation is this: A marginal is the slope of the total curve. Marginal is another term for slope.The general relation between total and marginal surfaces throughout the study of economics, especially utility (total utility and marginal utility), cost (total cost and marginal cost), revenue (total revenue and marginal revenue), and consumption (consumption expenditures and marginal propensity to consume). Making Tacos| Total and Marginal Product | 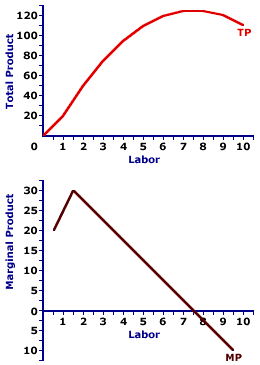 |
This two-paneled graph for the hourly production of Super Deluxe TexMex Gargantuan Tacos (with sour cream and jalapeno peppers) that visually illustrates the connection between total product and marginal product.- For the first few quantities of the variable input (the number of workers), total product in the top panel is positive AND the slope of the total product curve increases, it becomes steeper. This corresponds with a positive and increasing marginal product in the bottom panel.
- For the next several quantities of the variable input, the slope of the total product curve flattens out, although positive, the slope decreases. This corresponds to a decreasing marginal product in the bottom panel.
- For the last few quantities of the variable input, the slope of the total product curve in the top panel is negative. This corresponds with a negative marginal product in the bottom panel.
The Law of Diminishing Marginal ReturnsThe prime conclusion to drawn from this is the key role played by the law of diminishing marginal returns in the slope of both the marginal product curve and the total product curve. The "hump shape" of the marginal product curve is a direct reflection of first increasing marginal returns, as marginal product rises to a peak, then decreasing marginal returns and the onset of the law of diminishing marginal returns as marginal product falls.However, because the marginal product curve is essentially a plot of the slope of the total product curve, the shape of the total product curve also reflects the law of diminishing marginal returns. The increasingly steep slope of the total product curve for small quantities of the variable input is due to increasing marginal returns. Then with the onset of the law of diminishing marginal returns causes the total product curve to flatten out and subsequently turn down.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL PRODUCT AND MARGINAL PRODUCT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the downtown area trying to buy either shoe laces for your snow boots or a rim for your spare tire. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Mark Twain said "I wonder how much it would take to buy soap buble if there was only one in the world."
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
EJ
Economic Journal
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


