
|
|
INDUSTRY: A collection of firms that produce similar products sold in the same market. The concept of industry is most often used synonymously with market in most microeconomic analysis. That is, the study of perfect competition or oligopoly is not only the study of market structures, but also the study of industrial structure.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           BANK LIABILITIES: What a bank owes, including most notably customer deposits. Bank liabilities are typically listed on the right-hand side of a bank's balance sheet. Bank assets, what a bank owns, are listed on the left-hand side of a bank's balance sheet. Net worth is the difference between assets and liabilities. The most important liability category of most bank is checkable deposits, which is part of the economy's M1 money supply. The largest liability category includes other types of deposits (especially savings deposits, certificates of deposit, and money market deposits) that enter into the M2 and M3 monetary aggregates. Bank liabilities are the debts incurred by a bank, what a bank owes. While a bank is bound to have traditional business liabilities and debts (for electricity, office supplies, employee wages), the bulk of a bank's liabilities are financial--legal claims or IOUs issued by the bank. The most important liability category is deposits--financial wealth that others have placed with the bank for safekeeping. The bank owes this wealth to these depositors.A Representative, Hypothetical Balance Sheet| OmniBank Balance Sheet | 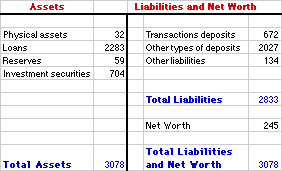 |
Before getting into the details of bank liabilities, consider this representative, hypothetical balance sheet for OmniBank (a representative, hypothetical bank) presented in the exhibit to the right. Like any balance sheet this one for the OmniBank is divided into two sides--assets on the left and liabilities and net worth on the right. As a "balance" sheet, both sides are equal--they balance. The assets on the left-hand side of the balance sheet are what OmniBank owns. Liabilities on the right-hand side of the balance sheet are what OmniBank owes. Net worth, also on the right-hand side of the balance sheet, is then the difference between assets and liabilities. In effect, net worth is what the bank owes to the owners of OmniBank. As a profit-seeking business, OmniBank's primary duty is to adjust these assets and liabilities to acquire profit. Of course, ALL businesses acquire profit by adjusting assets and liabilities. They boost revenue assets and reduce cost liabilities. But, unlike other types of producers, banks do not make adjustments with real production. In fact, the accounting process of adjusting entries in the balance sheet IS OmniBank's production. OmniBank's business is to change these entries. Three Liabilities| OmniBank Liabilities | 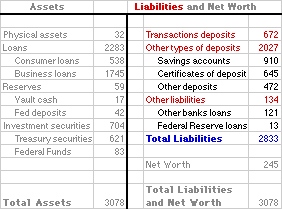 |
Now consider the primary liability categories for a bank. OmniBank liabilities are, of course, what the bank owes. OmniBank, being a representative bank, has three main categories of liabilities listed on the balance sheet at the right:- Transactions Deposits: The most important liability is transactions deposits. This, of course, is the technical name for checking accounts or checkable deposits. Make note that while checking accounts are assets for customers, they are liabilities for OmniBank. OmniBank owes these deposits to customers. Transaction deposits deserve a separate listing in the balance sheet because they are part of the M1 money supply.
- Other Types Of Deposits: As a full-service bank, OmniBank has other types of deposits, too. OmniBank offers savings accounts, certificates of deposit, money market deposits, repurchase agreements, and a host of other accounts that find their way into the M2 and M3 monetary aggregates.
- Other Liabilities: Most banks also have a few other liabilities. Specifically OmniBank might borrow from sources other than typical household and business customers that provide deposits. Two common sources of funds are Federal funds loans (loans from other banks) and Federal Reserve loans (loans from the Federal Reserve System).

Recommended Citation:BANK LIABILITIES, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLACK DISMALAPOD
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing about a thrift store seeking to buy either a genuine fake plastic Tiffany lamp or a microwave over that won't burn your popcorn. Be on the lookout for small children selling products door-to-door.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Much of the $15 million used by the United States to finance the Louisiana Purchase from France was borrowed from European banks.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
BJE
Bell Journal of Economics
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


