
|
|
EQUILIBRIUM: The state that exists when opposing forces exactly offset each other and there is no inherent tendency for change. Once achieved, an equilibrium persists unless or until it is disrupted by an outside force.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           DEMAND DECREASE: A decrease in the willingness and ability of buyers to purchase a good at the existing price, illustrated by a leftward shift of the demand curve. A decrease in demand is caused by a change in a demand determinant and results in a decrease in equilibrium quantity and a decrease in equilibrium price. A demand decrease is one of two demand shocks to the market. The other is a demand increase. A demand decrease results from a change in one of the demand determinants. The leftward shift of the demand curve disrupts the market equilibrium and creates a temporary surplus. The surplus is eliminated with a lower price. The comparative static analysis of the demand decrease is that equilibrium quantity decreases and equilibrium price decreases.Demand DeterminantsA decrease in demand can result from a change in any of the five demand determinants. - Buyers' Income: A decrease in buyers' income for a normal good or an increase in buyers' income for an inferior good.
- Buyers' Preferences: A decrease in buyers' preferences for the good.
- Other Prices: A decrease in the price of a substitute-in-consumption or an increase in the price of a complement-in-consumption.
- Buyers' Expectations: Expectations by buyers of a decrease in the price in the future.
- Number of Buyers: A decrease in the number of buyers in the market.
Old to NewFirst, consider the simple comparative static analysis of the demand decrease. The diagram at the right presents the Shady Valley market for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes. The initial equilibrium price is Po and the initial equilibrium quantity is Qo. This market equilibrium, of course, persists until and unless a determinant changes, which is the nature of equilibrium. The particular change under scrutiny is a decrease in demand caused by a change in any of the five demand determinants noted above. | Comparative Statics | 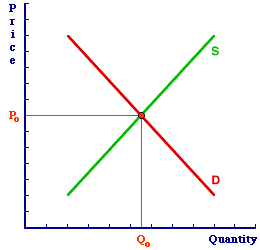 |
Suppose, for example, that the price of Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan Pie declines. Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan Pie is a prime, number one substitute for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes. To top off a tasty meal, buyers can buy a freshly prepared Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae or they can go for a piping hot Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan Pie. They buy one or they buy the other. This is how substitutes-in-consumption work. If the price of one substitute-in-consumption (Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan Pie) declines, the quantity demanded (of Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan) increases. But with more Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan satisfying after dinner dessert cravings, there is less demand for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes. As such, the demand for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes decreases. And when demand decreases, the original market equilibrium is disrupted. How is the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae market affected? A decrease in the price of a substitute-in-consumption works through the other prices demand determinant to shift the demand curve leftward. Click the [Demand Decrease] button to illustrate the leftward shift of the demand curve. The OLD market equilibrium is no longer equilibrium. A NEW market equilibrium is found at the intersection of the original supply curve and the new demand curve. Click the [New Equilibrium] button to highlight this result. The new equilibrium price is Pe and the new equilibrium quantity is Qe. Note that the price is lower and the quantity exchanged is less. Step by StepNow, consider how this demand shock to the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae market can be divided into six steps using the exhibit to the right. While the directions of the changes may differ, these six steps apply to the comparative static analysis of other demand and supply shocks. | Six Steps |  |
- First, a determinant changes. In this case, a decrease in the price of Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan activates a change in the other prices demand determinant. A determinant change ALWAYS starts the market adjustment process.
- Second, the determinant change causes a curve to shift. The decrease in the price of Double-Dot Carmel Fudge Pecan decreases the demand for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae and causes a leftward shift of the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae demand curve. Click the [Demand Decrease] button to illustrate this shift.
- Third, the shifted curve disrupts the market equilibrium, causing either a shortage or a surplus. In this example, the decrease in demand creates a surplus. While buyers are now willing and able to buy fewer Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes, sellers continue supplying the original quantity at the original price. Up to this point, they have no reason to change. Click the [Surplus] button to highlight this imbalance.
- Fourth, the market imbalance causes the price to change. In this case, the sellers are not able to sell all of the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes that they would like. As such, they are willing and able to sell Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes at a lower price. Click the [Price Decrease] button to illustrate this result.
- Fifth, the change in price causes changes in both quantities demanded and supplied. In this Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae market, the lower price has the intended effect of increasing the quantity demanded--which is the law of demand. It also has the unintended effect of decreasing the quantity supplied--which is the law of supply. Note that while the other prices determinant induces buyers to demand less at all prices, including the original equilibrium price, the price decrease causes the quantity demanded to subsequently rise.
- Sixth, changes in the quantities demanded and supplied both act to eliminate the market disequilibrium. In this example, the increase in the quantity demanded and the decrease in the quantity supplied eliminate the surplus. The price will continue to change as long as the market is out of balance with a surplus. The new equilibrium price at Pe is lower and the new equilibrium quantity at Qe is smaller. Click the [New Equilibrium] button to highlight this result.
One of EightA demand decrease is one of eight market disruptions--four involving a change in either demand or supply and four involving changes in both demand and supply. The other three single shift disruptions are demand increase, supply increase, and supply decrease. The four double shifts are demand and supply increase, demand and supply decrease, demand increase and supply decrease, and demand decrease and supply increase.

Recommended Citation:DEMAND DECREASE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
RED AGGRESSERINE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a flea market wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from long-lost relatives.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
There were no banks in colonial America before the U.S. Revolutionary War. Anyone seeking a loan did so from another individual.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
FCLT
Functional Central Limit Theorem
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


