
|
|
SPECIAL DRAWING RIGHTS: A system of accounts nations have with International Monetary Fund that are used to settle any balance of payments deficits. In essence, SDRs are simply an international currency that makes it easier to conduct all sorts of international transactions. In decades past, when gold was used as the primary international currency, any balance of payments deficits was paid with gold. However, in 1967 this system of SDRs was established in lieu of sending gold all over the globe.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           EQUILIBRIUM PRICE: The price that exists when a market is in equilibrium. Equilibrium price is simultaneously equal to both the demand price and supply price and it is the price that equates the quantity demanded and quantity supplied. In a market graph, the equilibrium price is found at the intersection of the demand curve and the supply curve. Equilibrium price, also commonly referred to as the market-clearing price, is one of two equilibrium variables. The other is equilibrium quantity. Equilibrium price is the price that achieves a market balance. Because quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal at the equilibrium price, there is no shortage nor surplus in the market, which means that neither buyers nor sellers are inclined to change the price, which is the primary condition for equilibrium.Moreover, because the equilibrium price also simultaneously equates the demand price and supply price, the market equilibrium generates an efficient allocation of resources (presuming competition and no market failures). The MarketThe market model displayed in the exhibit here can be used to identify the equilibrium price. This particular model represents the market for 8-track tapes, which are filled with the works of classic performers such as The Carpenters and Englebert Humperdink. The buyers and sellers happen to be folks attending the 88th Annual Trackmania 8-Track Tape Collectors Convention at the Shady Valley Exposition Center.| Equilibrium Price | 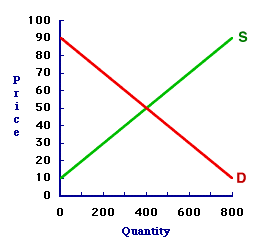
|
Before getting to the equilibrium price consider the market itself. - First, the demand curve (D) is negatively sloped--higher prices correspond with smaller quantities. This negative slope indicates the law of demand.
- Second, the supply curve (S) is positively sloped--higher prices correspond with large quantities. This positive slope indicates the law of supply.
Clearing the MarketEquilibrium price achieves a balance in the market, which is equality between quantity demanded and quantity supplied. It clears the market of any shortage or surplus. The only price that accomplishes this task is at the intersection of the demand curve and supply curve. This intersection point, and the price that achieves it, can be identified by clicking the [Equilibrium Price] button in the exhibit.Doing so reveals that the equilibrium price is 50 cents. At this price, the demand curve and supply curve intersect. The quantity demanded is 400 tapes and the quantity supplied is 400 tapes. The quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. The buyers can buy all that they want, so there is no shortage. The sellers can sell all that they want, so there is no surplus. Neither buyers nor sellers are motivated to change the price. The forces of demand and supply are in balance. This is the ONLY price that achieves a balance between these two quantities. Best of all, because this is equilibrium, the equilibrium price of 50 cents does not change and the equilibrium quantity of 400 tapes does not change unless or until an external force intervenes.

Recommended Citation:EQUILIBRIUM PRICE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GRAY SKITTERY
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time driving to a factory outlet wanting to buy either a coffee cup commemorating yesterday or a replacement remote control for your television. Be on the lookout for a thesaurus filled with typos.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Post WWI induced hyperinflation in German in the early 1900s raised prices by 726 million times from 1918 to 1923.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
IRBNE
Income Received But Not Earned
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


