
|
|
OFFICE OF MANAGEMENT AND BUDGET: An office within the Executive branch (specifically within the Office of the White House), that assists the President in various fiscal matters. Established in 1970, the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is responsible for developing the President's annual budget request to Congress, managing the Executive Branch, and evaluating Federal government regulations. The OMB staff are appointed by the President, but unlike other appointments, they do not need Senate confirmation. The duty of preparing the fiscal budget, and what this means for fiscal policy, has made the director of the OMB one of the more influential economic positions in country, ranking just a notch below the Chairman of the Federal Reserve System's Board of Governors and the Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisors. The Congressional counterpart of the OMB is the Congressional Budget Office (CBO).
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARGINAL ANALYSIS: A basic technique used in economics that analyzes small, incremental changes in key variables. Marginal analysis is the primary analytical approached used in the study of markets, production, consumption, business cycles, and economic policies. It not only reflects how most economic decisions are made, it also lends itself to mathematical and graphical analysis. Marginal analysis is based on a simple question often posed in the study of economics: "What happens if something changes by one dollar, one unit, one person, or one whatever?" For example, what happens to the quantity demanded of hot fudge sundaes if the market price',500,400)">market price increases by one cent? Or what happens to gross domestic product if investment decreases by $1? Or what happens to the market price of computers if one more computer supplier enters the industry?Marginal ObsessionThe apparent economic obsession with marginal changes exists for at two notable reasons.- Incremental Decisions: One reason is that many economic decisions made in the real world are made "at the margin." Duncan Thurly decides whether or not to eat one more slice of pizza at the all-you-can-eat pizza lunch buffet after having eaten five slices. Winston Smythe Kennsington III decides whether or not to hire an additional worker to the current staff. The Shady Valley City Council debates over adding an extra penny to their existing sales tax. These are marginal decisions, one and all, and just the sort of phenomena investigated with marginal analysis.
- Sophisticated Analysis: A second reason for using marginal analysis can best be termed analytical sophistication. Economists frequently make use of high-powered mathematical techniques, especially calculus, to create models of markets, consumer behavior, production decisions, or the aggregate economy. Such high-powered mathematical techniques not only lend themselves easily to analyzing incremental changes, but also to building extremely complex models that use these incremental changes to reveal interactions, implications, and conclusions about the economy that are often far from obvious. For example, such a complex model might reveal how a financial crises in Asia affects the construction of new homes in California.
Marginal Slope| Slope and Marginal | 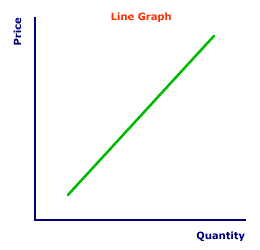 |
The use of marginal analysis works nicely with both mathematical and graphical analysis. Marginal means incremental change. In simple mathematical terms the slope parameter of an equation captures the marginal change. In a graph, the slope of a line captures a marginal change. In effect, the term "marginal" is synonymous with the term "slope."Consider this simple equation that captures a linear relation between two variables X and Y: Y = a + bX The key point of focus is the slope parameter, b. This equation indicates that each 1 unit change in X results in a change in Y by the value of b. If b is 4, then an increase in X by 1 results in Y increasing by 4. The slope parameter b captures the marginal change in Y resulting from a change in X.Now consider a simple graph of a line such as Y = a + bX. It too captures marginal change as the slope. This exhibit displays a positively-sloped line. The numerical value of the slope of the line is 4. This value captures the marginal change in Y measured on the vertical axis resulting from a change in X measured on the horizontal axis. An increase in X by 1 results in Y increasing by 4.

Recommended Citation:MARGINAL ANALYSIS, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
RED AGGRESSERINE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a flea market wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from long-lost relatives.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
North Carolina supplied all the domestic gold coined for currency by the U.S. Mint in Philadelphia until 1828.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
HSB
High School and Beyond
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


