
|
|
SCARCE RESOURCE: A resource with an available quantity less than its desired use. Scarce resources are also called factors of production. Scarce goods are also termed economic goods. Scarce resources are used to produce scarce goods. Like the more general society-wide condition of scarcity, a given resource is scarce because it has a limited availability in combination with a greater (potentially unlimited) productive use. It's both of these that make it scarce. In other words, even though an item is quite limited it will not be a scarce resource if it has few if any uses (think pocket lint and free good).
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MIXED ECONOMY: An economy, or economic system, that relies on both markets and governments to allocate resources. Every economy in the real world regardless of their common designation (such as capitalism, socialism, or communism) make use of both markets and governments and is technically a mixed economy. While, in theory, resource allocation could be undertaken exclusively through markets or exclusively through governments, in the real world all economies rely on a mix of both markets and governments for allocation decisions. Markets allocate resources through voluntary choices made by living, breathing people. Governments force allocation through involuntary taxes, laws, restrictions, and regulations. While everyone likely has their own personal favorite when it comes to using of markets or government to do the deed of allocation, both institutions play vital roles in a mixed economy.MarketsThe key term for markets is voluntary. Markets are the voluntary exchange of goods. No one forces a person to buy a hot fudge sundae for breakfast or work as a sales clerk at the jogging shoe boutique. People do a market exchange because they choose to.An economy that uses nothing but markets to allocate resources is called a pure market economy. This is a theoretical ideal that does not actually exist in the real world. But it provides an excellent benchmark for comparison with real world economies. Economists love benchmarks such as this, especially when practicing normative economics. GovernmentsThe key term for government allocation is involuntary. Governments set forth the laws and rules. If people do not follow the rules, then they are punished. Governments can punish those who do not follow the rules because... well... because that is what they do. Given a choice, people probably would rather NOT pay taxes or have their cars safety inspected. They follow government rules because they have to, because it is the law.An economy that uses nothing but government to allocate resources is called a pure command economy. This is also a theoretical extreme that does not actually exist in the real world. But like a pure market economy, it provides a benchmark for comparison with real world economies. A Real World Continuum| Mixed Economies | 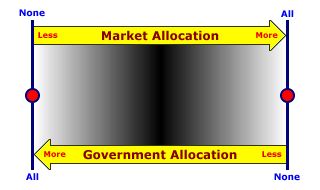 |
If pure market economies and pure command economies are theoretical ideals that do not actually exist in the real world, where does that leave real world economies? Somewhere in the middle. Real world economies form a continuum bounded by these two theoretical extremes.However, noting that real world economies are real and not theoretical ideals does not say much. While all real world economies are mixed, some mixed economies tend to use markets more than governments and others rely more on governments than markets. For example, capitalism is the popular term for a market-oriented economy that leans heavily to the market end. Socialism and communism are mixed economies that lean more (often a lot more) toward government control. Goals and PoliciesAn inherent dimension of a mixed economy is the pursuit of economic goals using assorted government policies. The five basic goals that are generally desired by society are: (1) full employment, (2) stability, (3) economic growth, (4) efficiency, and (5) equity. Governments take primary responsibility in the pursuit of these five goals with a wide variety of economic policies that assist, guide, control, and regulate voluntary market exchanges. Such policies take the form of: (1) laws passed by legislatures, (2) administrative actions taken by elected executives, (3) rules set forth by government agencies, and (4) decisions made through the courts.

Recommended Citation:MIXED ECONOMY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
RED AGGRESSERINE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a flea market wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from long-lost relatives.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Rosemary, long associated with remembrance, was worn as wreaths by students in ancient Greece during exams.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
BA
Bank Acceptance
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


