
|
|
BARTER ECONOMY: An economy that trades goods and services using barter exchanges rather than money. Barter economies originally predated the invention of money, emerging out the early stage of self-sufficiency before giving way to the use of commodity money. However, barter economies occasionally surface in modern times, especially when the public loses confidence in the monetary unit during a government crises or a period of hyperinflation.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           PRICE LEVEL: The average of the prices of goods and services produced in the aggregate economy. In a theoretical sense, the price level is the price of aggregate production. In a practical sense, the price level is commonly measured by either of two price indexes, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the GDP price deflator. The CPI is the price index widely publicized in the media and used by the general public. The GDP price deflator, in contrast, is less well-known, but is usually the price index of choice among economists. The inflation rate is calculated as the percentage change in the price level. The price level is a theoretical or conceptual average of the prices of goods and services produced and/or consumed in the economy. It forms the basis for estimating inflation and plays a key role in modern macroeconomic analysis. The price level was explicitly incorporated into macroeconomic analysis with the introduction of aggregate market. This model which was designed to provide insight into the inflation of the 1970s and replaced earlier Keynesian economic analysis that focused more on the problem of unemployment.Price Level and Market Price| Aggregate Market | 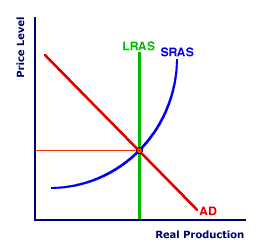 |
The price level plays a similar role in the aggregate market that price plays in the standard market analysis. The aggregate demand (AD) curve captures the relation between the price level and the amount of real GDP demanded by the four economic sectors (household, business, government, and foreign). The aggregate supply curves (SRAS and LRAS) capture the short-run and long-run relations between the price level and the amount of real GDP produced in the macroeconomy. In the graphical presentation of the aggregate market, the price level (generally measured by the GDP price deflator) is displayed on the vertical axis (with real GDP on the horizontal axis).However, unlike standard microeconomic markets, the price level is not an observable characteristic of the world, but something that must be derived. For example, identifying the price of a Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae is as simple as observing a market transaction between buyer and seller. The market price of a Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae is the price the buyer pays the seller. In contrast, the aggregate market is very much a theoretical construct. There is NO physical aggregate market presence in which the exchange of one unit of real GDP at a corresponding price level can be observed. The price level is the average of millions of different prices. And this price level must be calculated. Price IndexIn principle, calculating the average of a bunch of prices seems relatively straightforward. In practice, however, this can be quite involved. Two problems are worth noting.- First is the task of gathering data on the prices to be averaged. The price level is an average of hundreds of thousands of different prices. The needed data can be estimated by sampling prices paid for a given market basket of goods, which is the method used by the CPI each month. Or the data can be derived in a more comprehensive fashion, which is how the GDP price deflator is calculated each quarter (along with gross domestic product and related measures).
- Second is the question of how best to "average" the prices. One way is to compute a simple arithmetic average, or what can be term an unweighted average. This is accomplished by adding all prices then dividing by the total number of goods. Another way is to weight the prices with the quantity of the good produced, consumed, or exchanged. This is the accepted method for both the CPI and the GDP price deflator.
To see why a weighted average is the preferred averaging method, consider the average of two prices. Suppose that hot fudge sundaes sell for $2, and cars sell for $20,000. The simple unweighted average of these two prices is $10,001 (= $20,002/2). But what on earth does this $10,001 number mean? An unweighted average for all prices of all goods produced in the economy--for cars, hot fudge sundaes, toothpicks, nuclear reactors, soft drinks, houses, compact disks, airplanes--might generate a number, such as $547.33 that has no real meaning. On average the price paid for a good is $547.33, but this average provides little useful information. And most important, a change in this "average" from one year to the next, gives little insight into inflation.In contrast, a weighted average--with the weights being the quantities of goods produced, consumed, or exchanged--does provide greater insight. In effect, a weighted average is the total expenditure on aggregate production. If this total expenditure changes, with no change in the quantity weights, then a clear indication of changes in the price level and inflation can be had. That is reason that the price level is computed as a weighted average, or as a price index, for both the CPI and the GDP price deflator. The CPI weights each price with the quantity purchased by urban consumers. The GDP price deflator weights the prices with the quantities produced and sold to the household, business, government, and foreign sectors.

Recommended Citation:PRICE LEVEL, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 1, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GREEN LOGIGUIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the shopping mall seeking to buy either storage boxes for your computer software CDs or a set of tires. Be on the lookout for small children selling products door-to-door.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Junk bonds are so called because they have a better than 50% chance of default, carrying a Standard & Poor's rating of CC or lower.
|

|
|
"Experience keeps a dear school, but fools will learn in no other. " -- Benjamin Franklin
|

|
IO
Industrial Organization
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


