
|
|
ASSOCIATION OF SOUTHEAST ASIAN NATIONS: The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a subregional organization established in 1967 in Bangkok by the five original Member Countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. Brunei Darussalam joined in 1984, Vietnam in 1995, Laos and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999. The aims and purposes of the Association are to accelerate the economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region and to promote regional peace and stability through abiding respect for justice and the rule of law.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           SLOPE, NET EXPORTS LINE: The negative slope of the net exports line is based on the marginal propensity to import (MPM). Because net exports are exports minus imports, the induced change in imports causes an opposite change in net exports. As such, the slope of the net exports line is negative, less than zero (but greater than negative one). The slope of the net exports line affects the slope of the aggregate expenditures line and thus also affects the magnitude of the multiplier process. | Net Exports Line | 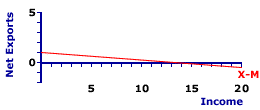
|
The net exports line shows the relation between net exports by the foreign sector and the level of aggregate domestic income or production. The income and production measures most commonly used are national income and gross domestic product.A representative net exports line is presented in the exhibit to the right. This red line, labeled X-M in the exhibit, is negatively sloped, indicating that greater levels of income or production generate smaller levels of net exports by the foreign sector. This negative relation indicates that imports, which are subtracted from exports to derived net exports, are induced by an expanding economy. The net exports line graphically illustrates the net exports-income relation for the foreign sector, which is then added to the consumption line to derive the aggregate expenditures line used in Keynesian economics to identify equilibrium income and production. The slope of the net exports line presented here is negative. In fact, the slope of the net exports line is numerically equal to the negative of the marginal propensity to import. In this case the slope is equal to -0.075. The negative slope reflects induced net exports--more income means fewer net exports. Click the [Slope] button to illustrate. To illustrate the equality between slope and the negative of the marginal propensity to import, consider the equations for each. The slope of the net exports line is specified as the "rise" over the "run." The rise is the change in net exports measured on the vertical axis and the run is the change in income measured on the horizontal axis. However, because exports are autonomous, the only income induced change in net exports comes from imports, in a negative way. | slope | = | rise
run | = | change in net exports
change in income | = - | change in imports
change in income |
The marginal propensity to import (MPM) is the incremental change in net exports resulting from an incremental change in income. | MPM | = | change in imports
change in income |
The negative slope of the net exports line is the marginal propensity to import, or the slope of the net exports line is the negative of the marginal propensity to import, on is the negative of the other.The negative slope of the net exports line reflects induced net exports, which is net exports that depend on the level of income. If the aggregate economy has more income, then the foreign sector is induced to undertake fewer net exports. Of course, a drop in aggregate income induces the foreign sector to increase net exports.

Recommended Citation:SLOPE, NET EXPORTS LINE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 1, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GREEN LOGIGUIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the shopping mall seeking to buy either storage boxes for your computer software CDs or a set of tires. Be on the lookout for small children selling products door-to-door.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
A half gallon milk jug holds about $50 in pennies.
|

|
|
"Experience keeps a dear school, but fools will learn in no other. " -- Benjamin Franklin
|

|
SMA
Structural Moving Average
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


