
|
|
VERY LONG RUN, MICROECONOMICS: A production time period in which all inputs are variable, including those under control of the firm and those beyond the control of the firm. During the very long run, not only are the labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship inputs variable, but so too are key production inputs such as government rules, technology, and social customs. This is one of four production time periods used in the study of microeconomics. The other three are short run, long run, and very short run.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL COST AND MARGINAL COST: A mathematical connection between marginal cost and total cost stating that marginal cost IS the slope of the total cost curve. This relation between total cost and marginal cost is also seen with total variable cost. The slope of the total variable cost curve is marginal cost, as well. The relation between total cost and marginal cost is but another in the long line of applications of the total-marginal relation. | Total Cost and Marginal Cost | 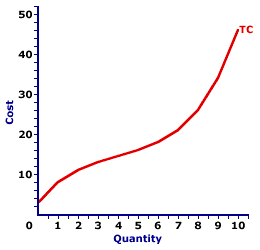 | 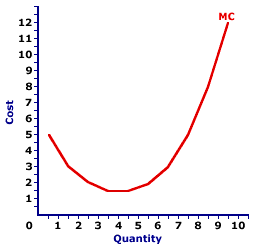 |
The slope of the total cost curve (and total variable cost curve) is marginal cost. As such, if the total cost curve has a positive slope (that is, is upward sloping), then marginal cost is positive. Moreover, if the total cost curve has a positive and increasingly steeper slope, then the marginal cost is positive and rising. If the total cost curve has a positive and increasingly flatter slope, then the marginal cost is positive but falling. This particular total-marginal relation applies to both total cost and total variable cost. Because not only is marginal cost the slope of the total cost curve, it is also the slope of the total variable cost curve. The reason is that any changes in total cost resulting from changing output is matched by changes in total variable cost. This occurs because total fixed cost is FIXED. This two-paneled graph for the production of Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos (those cute and cuddly armadillos and rattlesnakes) visually illustrates the connection between total cost and marginal cost. For the first few quantities of output (Stuffed Amigos), total cost in the top panel is positive AND the slope of the total cost curve decreases--it becomes flatter. This corresponds with a positive and decreasing marginal cost in the bottom panel up to 4 Stuffed Amigos. For the next several quantities of Stuffed Amigos output, the slope of the total cost curve becomes increasingly steeper. This corresponds to an increasing marginal cost in the bottom panel. The prime conclusion is the key role played by the law of diminishing marginal returns in the slope of both the marginal cost curve and the total cost curve. - The U-shape of the marginal cost curve is a direct reflection of first increasing marginal returns, as marginal cost falls to a minimum, then decreasing marginal returns and the onset of the law of diminishing marginal returns as marginal cost rises.
- However, because the marginal cost curve is a plot of the slope of the total cost curve, then the shape of the total cost curve also reflects the law of diminishing marginal returns. The flattening slope of the total cost curve for small quantities of output is due to increasing marginal returns. Then the onset of the law of diminishing marginal returns causes the total cost curve to become increasingly steeper.
While this diagram relates marginal cost and total cost, the same story applies to the relation between marginal cost and total variable cost. Marginal cost is also the slope of the total variable cost curve. As such, the shape of the total variable cost curve is also a reflection of increasing, then decreasing marginal returns.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL COST AND MARGINAL COST, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLUE PLACIDOLA
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads looking to buy either a wall poster commemorating the first day of winter or blue cotton balls. Be on the lookout for rusty deck screws.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
General Electric is the only stock from the original 1896 Dow Jones Industrial Average remaining in the current index.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
AFBD
Association of Futures Brokers and Dealers (UK)
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


