
|
|
LOCATION THEORY: A theoretical framework for studying the location decisions made of firms and households based on transportation cost and spatial differences in the accessibility of inputs and markets for outputs. Location theory, developed with noted contributions from August Losch, Alfred Weber, Johann von Thunen, Walter Christaller, and Walter Isard, explicitly considers the cost of transportation in the production and consumption choices made by firms and households. Location theory has been used to explain urban density, labor migration, and land use.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL COST CURVE: A curve that graphically represents the relation between the total cost incurred by a firm in the short-run production of a good or service and the quantity produced. The total cost curve is a cornerstone upon which the analysis of short-run production is built. It combines all opportunity cost of production into a single curve, which can then be used with the total revenue curve to determine profit. The marginal cost curve, THE focal point for the analysis of short-run production, is derived directly from the total cost curve. The shape of the curve reflects increasing marginal returns at small quantities of output and decreasing marginal returns at larger quantities. The total cost curve graphically represents the relation between total cost and the quantity of production. This curve can be derived in two ways. One is to plot a schedule of numbers relating output quantity and total cost. The other is to vertically add the total variable cost curve and the total fixed cost curve. The slope of the total cost curve is marginal cost. When constructing this curve, it is assumed that total cost changes as a result of changes in the quantity of output produced, while other variables like technology and resource prices are held fixed.| Total Cost Curve | 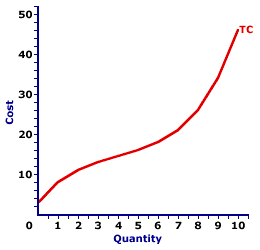 |
The graph at the right is the total cost curve for the short-run production of Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos (those cute and cuddly lizards, snakes, armadillos and tarantulas). The quantity of Stuffed Amigos production, measured on the horizontal axis, ranges from 0 to 10 and the total cost incurred in the production of Stuffed Amigos, measured on the vertical axis, ranges from $3 to $46.The most striking feature of the total cost curve is its curvature. The total cost curve emerges from the vertical axis at $3, then twists and turns its way to $46. This curve begins relatively steep, then flattens, before turning increasingly steep once again. It is somewhat reminiscent of the total product curve. The reason is that both curves are guided by the law of diminishing marginal returns. A scenic trip along this curve reveals that the slope of the total cost curve flattens as the first four Stuffed Amigos are produced. This range of output corresponds with increasing marginal returns found in Stage I of production. Increasing marginal returns is what causes the total cost curve to flatten. Continuing this trip shows that the slope of the total cost curve becomes increasingly steeper after the fourth Stuffed Amigo is produced. Steeper and steeper. This range of output corresponds with decreasing marginal returns, and the extremely important law of diminishing marginal returns, found in Stage II of production. Deceasing marginal returns is what causes the total cost curve to become steeper and steeper and steeper. The total cost curve is frequently used with a total revenue curve to determine the profit maximizing level of production for a firm. However, this curve is perhaps most important as the basis for deriving the average total cost curve and the marginal cost curve. In particular, marginal cost is the slope of the total cost curve.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL COST CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
PINK FADFLY
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time calling an endless list of 800 numbers wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for high interest rates.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Woodrow Wilson's portrait adorned the $100,000 bill that was removed from circulation in 1929. Woodrow Wilson was removed from circulation in 1924.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
SMSA
Standard Metropolitan Statistical Area
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


