
|
|
KEYNESIAN CROSS: The standard diagram used in Keynesian economics to identify the equilibrium level of aggregate output (that is, gross domestic product), with aggregate expenditures measured on the vertical axis, and aggregate output measured on the horizontal axis. This diagram contains two key lines, the aggregate expenditure line and the 45-degree line. Intersection between these lines indicates equilibrium aggregate output. This intersection, or cross, is what gives rise to the name.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           CHANGE IN SUPPLY: A shift of the supply curve caused by a change in one of the supply determinants. A change in supply is caused by any factor affecting supply EXCEPT price. A related, but distinct, concept is a change in quantity supplied. A change in supply is a change in the entire price-quantity relation that makes up the supply curve. It means that a different quantity supplied is paired with a given supply price or that a different supply price is paired with a given quantity supplied. The result of this repairing of prices and quantities is a repositioning, or a shift, of the supply curve.The five supply determinants (resource prices, production technology, other prices, sellers' expectations, and number of sellers) are responsible for causing a change in supply. In fact, the only thing that DOES NOT cause a change in supply is the supply price. Supply and Quantity SuppliedTo set the stage for an understanding of this difference, take note of two related concepts: - Supply: Supply is the range of quantities that sellers are willing and able to sell at a range of supply prices. It is ALL points that make up a supply curve.
- Quantity Supplied: Quantity supply is a specific quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell at a specific supply price. It is but ONE point on a supply curve.
Making ChangesSo what happens when the phrase "change in" is placed in front of each term?- Change in Supply: A change in supply is a change in the ENTIRE supply relation. This means changing, moving, and shifting the entire supply curve. The entire set of prices and quantities is changing. In other words, this is a shift of the supply curve. A change in supply is caused by a change in the five supply determinants.
- Change in Quantity Supplied: A change in quantity supplied is a change from one price-quantity pair on an existing supply curve to a new price-quantity pair on the SAME supply curve. In other words, this is a movement along the supply curve. A change in quantity supplied is caused by a change in price.
Changing Supply| A Change in Supply | 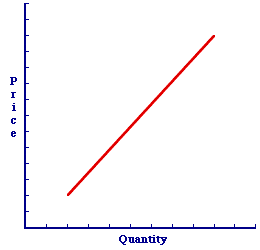
|
A change in supply is a shift of the supply curve. A change in quantity supplied is a movement along a given supply curve. These alternatives can be illustrated with the positively-sloped supply curve presented in this exhibit. This supply curve captures the specific one-to-one, law of supply relation between supply price and quantity supplied. The five supply determinants are assumed to remain constant with the construction of this supply curve.- A Change in Supply: A change in supply, which is triggered by a change in any of the five supply determinants, is a shift of the supply curve. Click the [A Determinant Change] button to demonstrate.
A Change in Quantity Supplied
: A change in quantity supplied, which is only triggered by a change in supply price, is a movement along the supply curve. Click the [A Price Change] button to demonstrate.An Important DifferenceWhy is this difference so important? The answer is as simple as cause and effect. The supply curve is used (together with demand) to explain and analyze market exchanges. The sequence of events follows a particular pattern.- First, a supply (or demand) determinant changes.
- Second, this determinant change causes the supply curve (or demand curve) to shift.
- Third, the change in supply (or demand) causes either a shortage or a surplus imbalance in the market. The market is in a temporary state of disequilibrium.
- Fourth, the shortage and surplus imbalance causes the price of the good to change.
- Fifth, the change in price causes a change in quantity supplied (and demanded).
- Sixth, the change in quantity supplied (and demanded) eliminates the shortage or surplus and restores market equilibrium.
The key conclusion is that supply (and demand) determinants, which induce changes in supply (and demand), are the source of instability in the market. The change in price, which induces a change in quantity supplied (and demanded) is the means of eliminating the instability and restoring equilibrium.

Recommended Citation:CHANGE IN SUPPLY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLUE PLACIDOLA
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads looking to buy either a wall poster commemorating the first day of winter or blue cotton balls. Be on the lookout for rusty deck screws.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The average bank teller loses about $250 every year.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
FSL
Federal Savings and Loan Association
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


