
|
|
GINI INDEX: One of the most common measures of income or wealth distributions. It indicates how equal, or unequal, income, wealth, or similar stuff is distributed among the population. If you happen to come across a Gini index, you'll see that it falls in the range of 0 to 1. A value of 0 tells you that the distribution is perfectly equal, that is, everyone has exactly the same amount of income, wealth, or whatever. A value of 1, however, tells you that the distribution is what we could call perfectly unequal, that is, one person has everything and everyone else has nothing.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           KEYNESIAN AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE: An aggregate supply curve--a graphical representation of the relation between real production and the price level--that reflects the basic principles of Keynesian economics. The Keynesian aggregate supply curve actually comes in two versions. The basic version is reverse-L shaped, with a horizontal segment connected to a vertical segment at a sharp corner. The modified version is also reverse-L shaped, but the vertical and horizontal segments have positive slopes and connecting corner is rounded. An alternative is the classical aggregate supply curve. An aggregate supply curve is a graphical representation of the relation between real production and the price level. Keynesian economics implies that the aggregate supply curve contains two segments. One segment is more or less horizontal, indicating that price rigidity in the downward direction results in a reduction in real production. The other segment is more of less vertical, indicating that full employment is more or less maintained at higher price levels.| Keynesian AS Curve | 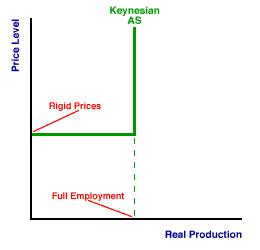
|
The exhibit to the right illustrates a basic Keynesian aggregate supply (AS) curve. The obvious characteristic is that the curve is shaped like a reserve L, with a horizontal segment joining a vertical segment at a sharp corner. The horizontal segment of the curve reflects the Keynesian notion that a decline in demand leads to a decline in real production, primarily because prices remain constant. The vertical segment is a recognition that the total quantities of resources are fixed and that total production is ultimately limited, which results in full employment.While this reverse-L shaped curve captures the original essence of Keynesian economics, the Keynesian view has changed over the years. A more refined version of the Keynesian aggregate supply curve can be illustrated by clicking the [New Keynesian AS Curve] button. This new curve retains the same basic reverse-L shape, but the horizontal segment has a slight, positive slope rather than being perfectly horizontal and the vertical segment has a steep, positive slope rather than being perfectly vertical. Moreover, the vertical and horizontal segments are joined by a curved segment rather than a sharp corner. This version of the Keynesian aggregate supply curve is both more realistic and looks a great deal like the short-run aggregate supply curve used in modern aggregate market analysis.

Recommended Citation:KEYNESIAN AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLACK DISMALAPOD
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing about a thrift store seeking to buy either a genuine fake plastic Tiffany lamp or a microwave over that won't burn your popcorn. Be on the lookout for small children selling products door-to-door.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
More money is spent on gardening than on any other hobby.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
LCH
Life Cycle Hypothesis
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


