
|
|
IMPERFECT COMPETITION: Any markets or industries that do not match the criteria for perfect competition. The key characteristics of perfect competition are: (1) a large number of small firms, (2) identical products sold by all firms, (3) freedom of entry into and exit out of the industry, and (4) perfect knowledge of prices and technology. These four characteristics are essentially impossible to match in the real world.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           RESOURCE QUANTITY, AGGREGATE SUPPLY DETERMINANT: One of three categories of aggregate supply determinants assumed constant when the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves are constructed, and which shifts both aggregate supply curves when it changes. An increase in a resource quantity causes an increase (rightward shift) of both aggregate supply curves. A decrease in a resource quantity causes a decrease (leftward shift) of both aggregate supply curves. The other two categories of aggregate supply determinants are resource quality and resource price. Specific determinants falling into this general category include population, labor force participation, capital stock, and exploration. Anything affecting the quantity of labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship is also included. This determinant category makes use of the relation between the quantity of limited resources available and the production of goods and services. With more resources, the economy is able to produce more output. With fewer resources, it is able to produce less output. The result is a change in the full-employment level of real production and shifts of both the SRAS and LRAS curves. In particular, if the economy has more resources, then aggregate supply increases and both aggregate supply curves shift rightward. With fewer resources, aggregate supply decreases and both curves shift leftward.Four ExamplesSome of the specific determinants that can cause changes in resource quantities include:- Population: The size in the total population, which is affected by births, deaths, and migration, is a key influence on the quantity of labor. A larger population means an increase in the number of potential workers. While population generally increases through both natural growth and immigration, it can decrease as well. Reasons for a declining population including emigration, wars, famines, diseases, and natural disasters.
- Labor Force Participation: The proportion of the population willing and able to engage in production is another key influence on the labor quantity. A change in this proportion changes the labor force and shifts both aggregate supply curves. The U.S. economy has seen an increase in its labor force participation rate over the last 50 years largely through an increase in the proportion of women in the labor force.
- Capital Stock: Changes in the economy's stock of capital is the most important influence on the quantity of capital. These changes are brought about through a combination of investment and depreciation. Investment adds to the capital stock and depreciation reduces it. Investment has the curious role of affecting both the aggregate demand curve, as one of the four aggregate expenditures, and the aggregate supply curves, by influencing the capital stock.
- Exploration: The discovery of new sources of raw materials or other natural resources influences the quantity of land. While the modern economy is unlikely to "discover" large masses of land like explorers did a few centuries back, exploration does identify mineral deposits, fossil fuel reserves, and other natural resources that increase aggregate supply. Alternatively, depletion of existing natural resources causes a decrease in aggregate supply.
Shifting the Curves| Shifting the SRAS Curve | 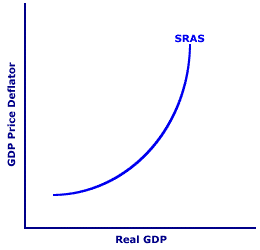 | Shifting the LRAS Curve | 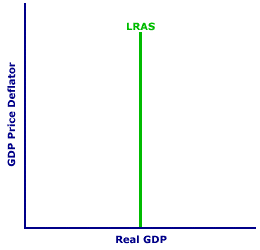 |
To illustrate how a resource quantity determinant like the stock of capital and size of the population shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve, consider the exhibit to the right. This exhibit displays a representative, positively-sloped short-run aggregate supply curve in the top panel and a standard, vertical long-run aggregate supply curve in the bottom panel. Like all aggregate supply curves, these are constructed based on several ceteris paribus aggregate supply determinants, such as the quantity of labor or capital. The key question is: What happens to these aggregate supply curves if resource quantity changes?More Resource QuantitySuppose, for example, that a resource quantity like population or the capital stock increases. This increase in a resource quantity means the full-employment level of real production increases. This leads to an increase in aggregate supply, causing both aggregate supply curves to shift rightward. Note that the increase in a resource quantity makes it possible to supply a larger quantity of real production at the same price level, which means an increase in aggregate supply.To see how an increase in resource quantity affects these aggregate supply curves, click the [More Resource Quantity] button. The greater resource quantity triggers an increase in aggregate supply and a rightward shift of both the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves. Less Resource QuantityAlternatively, suppose that population or the capital stock decreases. This decrease in a resource quantity means the full-employment level of real production also decreases. This leads to a decrease in aggregate supply, causing both aggregate supply curves to shift leftward. Note that the decrease in a resource quantity means a smaller quantity of real production is supplied at the same price level, which results in a decrease in aggregate supply.To see how a decrease in resource quantity affects these aggregate supply curves, click the [Less Resource Quantity] button. The smaller resource quantity triggers a decrease in aggregate supply and a leftward shift of both the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves. The Other Two DeterminantsResource quality is one of three categories of aggregate supply determinants. The other two are resource quantity and resource price. While resource quantity and resource quality affect both the long-run and short-run aggregate supply curves, resource price affects only the short-run aggregate supply curve.- Resource Quality: This determinant includes any ceteris paribus factors that affect the quality of labor, capital, land, or entrepreneurship used in production, including education and technology. An increase in resource quality increases aggregate supply and shifts both long-run and short-run aggregate supply curves to the right. A decrease shifts both curves to the left.
- Resource Price: This determinant includes any ceteris paribus factors that affect the price of labor, capital, land, or entrepreneurship used in production. Two most notable resource price determinants are wages and energy prices. A decrease in resource price increases aggregate supply and shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right. An increase shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.

Recommended Citation:RESOURCE QUANTITY, AGGREGATE SUPPLY DETERMINANT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GRAY SKITTERY
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time driving to a factory outlet wanting to buy either a coffee cup commemorating yesterday or a replacement remote control for your television. Be on the lookout for a thesaurus filled with typos.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Francis Bacon (1561-1626), a champion of the scientific method, died when he caught a severe cold while attempting to preserve a chicken by filling it with snow.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
BOA
Basic Ordering Agreement
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


