
|
|
COINCIDENT ECONOMIC INDICATOR: One of four economic statistics that tend to move up and down with the expansions and contractions of the business cycle. You can get a pretty good idea of what our economy's doing RIGHT NOW by looking at these. Coincident economic indicators are measurements that move with the aggregate economy. When a contraction starts, these indicators decline. During an expansion. these indicators rise. These indicators, and their siblings, leading economic indicators and lagging economic indicators are compiled by their parents, those pointy-headed economist at National Bureau of Economic Research.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TECHNOLOGY, AGGREGATE SUPPLY DETERMINANT: One of several specific aggregate supply determinants assumed constant when the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves are constructed, and that shifts both aggregate supply curves when it changes. An increase in technology causes an increase (rightward shift) of both aggregate supply curves. A decrease in technology causes a decrease (leftward shift) of both aggregate supply curves. Other notable aggregate supply determinants include wages, energy prices, and the capital stock. Technology comes under the resource quality aggregate supply determinant. Technology is the information and knowledge the economy has concerning production techniques and methods of combining scarce resources in the production of goods and services. While the term technology is often used in reference to the LATEST production techniques (especially when computers are involved), it actually refers to all techniques.Throughout most of history, technology has advanced forward. Through scientific research, production experience, and just plain learning-by-doing, society tends to know more today than yesterday. Technology advances. Of course technology can decline, such as what happened during the European medieval ages, but this is highly unusual. An advance in technology makes it possible to produce more output with a given quantity of resources or to produce the same quantity of output with fewer resources, hence causing an increase in both long-run and short-run aggregate supply. A less common decline in technology means producing less output with a given quantity of resources or to produce the same quantity of output with more resources, hence causing a decrease in both long-run and short-run aggregate supply. | Shifting the SRAS Curve | 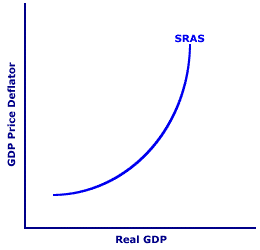 | Shifting the LRAS Curve | 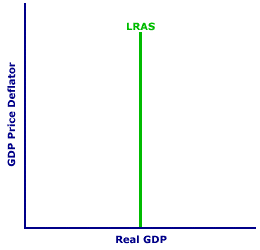 |
Consider a pair of typical aggregate supply curves, both long-run and short run, such as those displayed in the exhibit to the right. The exhibit displays a positively-sloped short-run aggregate supply curve in the top panel and a vertical long-run aggregate supply curve in the bottom panel. Like all aggregate supply curves, these are constructed based on several ceteris paribus aggregate supply determinants, such as technology. The key question is: What happens to these aggregate supply curves if technology changes?Advancing TechnologySuppose, for example, major breakthroughs in computer technology, much like those transpiring during the 1980s and 1990s, enhance the productive capabilities of virtually every industry in the economy. This advance in technology leads to an increase in aggregate supply, both short run and long run, causing both SRAS and LRAS curves to shift rightward. Note that the increase in technology means a larger quantity of real production is supplied at the same price level, which means an increase in aggregate supply.To see how better technology affects the aggregate supply curves, click the [Advancing Technology] button. The advance in technology triggers an increase in aggregate supply and a rightward shift of both the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves. Declining TechnologyAlternatively, suppose that the economy somehow loses a portion of its technological know how. A decline in technology is much less common in the modern economy than advancing technology, but it can happen. Suppose, for example, that a particularly viscous computer virus rapidly spreads throughout the economy, destroying a large portion of valuable digitally stored information.This decline in technology leads to a decrease in aggregate supply, both short run and long run, causing both SRAS and LRAS curves to shift leftward. Note again that the decrease in technology means a smaller quantity of real production is supplied at the same price level, which means a decrease in aggregate supply. To see how a drop off in technology affects the aggregate supply curves, click the [Declining Technology] button. The decline in technology triggers a decrease in aggregate supply and a leftward shift of both the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves. What Does It Mean?The importance of technology as an aggregate supply determinant is particularly important for the long run expansion of the economy. Technological advance has been one of the key reasons, if not THE key reason, that the modern economy has achieved current, historically unprecedented, living standards. The advent over the past two hundred years, of automobiles, pharmaceuticals, electric light bulbs, computers, airplanes, telephones, lasers, and other products on a lengthy list way too long to present here, have played an enormous part in making lives healthy, wealthy, and comfortable.This technological march that shifts the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves tends to be subtle and more often than not overwhelmed by business-cycle-inducing shifts of the aggregate demand curve. While it is easy to look back a few decades to note the pace of progress, changes are often overlooked as they occur, or if not, the changes are merely taken for granted. However, technological progress is not a given. Someone must make the effort needed to create new products and make them available to the public. If these folks are not compensated for their efforts, then they have no incentive to perform their innovative activities and technological progress ceases.

Recommended Citation:TECHNOLOGY, AGGREGATE SUPPLY DETERMINANT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 1, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BROWN PRAGMATOX
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time lost in your local discount super center trying to buy either clothing for your kitty cats or a set of luggage without wheels. Be on the lookout for infected paper cuts.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Lewis Carroll, the author of Alice in Wonderland, was the pseudonym of Charles Dodgson, an accomplished mathematician and economist.
|

|
|
"Experience keeps a dear school, but fools will learn in no other. " -- Benjamin Franklin
|

|
HSI
Hang Seng Index (Hong Kong)
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


