Average revenue is the revenue generated per unit of output sold. It plays a role in the determination of a monopolistically competitive firm's profit. Per unit profit is average revenue minus average (total) cost. A monopolistically competitive firm generally seeks to produce the quantity of output that maximizes profit.The relation between average revenue and quantity of output produced depends on market structure. For a perfectly competitive firm, average revenue is not only equal to price, but more importantly, it is equal to marginal revenue, all of which are constant. For a monopoly, monopolistic competition, or oligopoly firm, average revenue is greater than marginal revenue, both of which decrease with larger quantities of output. The constant or decreasing nature of average revenue is a prime indication of the market control of a firm.
Average revenue can be represented in a table or as a curve. For a monopolistically competitive firm, the average revenue curve is a negatively-sloped line. The average revenue curve is also the demand curve facing the firm.
The average revenue received by a firm is total revenue divided by quantity, often expressed as this simple equation:
| average revenue | = | total revenue
quantity |
At times, it can be helpful to turn this equation around and calculate total revenue from average revenue:
| total revenue | = | average revenue | x | quantity |
Monopolistic competition is a market structure with a large number of relatively small firms that sell similar but not identical products. Each firm is small relative to the overall size of the market such that it has some market control, but not much. In other words, it can sell a wide range of output at a narrow range of prices. This translates into a relatively elastic demand curve. If a monopolistically competitive firm wants to sell a larger quantity, then it must lower the price.Average Revenue,
Sandwich Style | 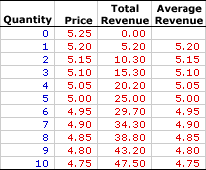 |
The table to the right summarizes the average revenue received by a hypothetical firm, Manny Mustard's House of Sandwich. Manny is one of thousands of restaurants in the greater Shady Valley metropolitan area that offers sandwiches and other meals to lunch-hungry buyers. Manny Mustard is a monopolistically competitive firm with minimal market control, facing a negatively-sloped demand curve. To sell a larger number of sandwiches, Manny Mustard must lower the price.The first column is the quantity of sandwiches sold, ranging from 0 to 10. The second column is the price Manny Mustard receives for selling his sandwiches, which ranges from $4.75 to $5.25 per sandwich. The third column is the total revenue Manny receives for producing and selling his sandwiches.
Average revenue in the forth column is found by dividing total revenue in the third column by quantity in the first column. For example, because the total revenue generated from the production of 5 sandwiches is $25, average revenue is $5 (= $25/5). Each value in the fourth column is calculated in the same way.
The obvious point is that average revenue decreases with the quantity of sandwiches sold. Moreover, average revenue is also equal to the price of sandwich for each quantity. The price of 5 sandwiches is $5 and the average revenue for 5 sandwiches is also $5. Average revenue is price. Price is average revenue. The two are one and the same.
Average Revenue Curve,
Sandwich Style | 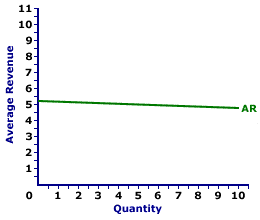 |
The average revenue curve for Manny Mustard is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that Manny Mustard is a monopolistically competitive seller of sandwiches and thus faces a negatively-sloped demand curve. Larger quantities of output are only possible with lower prices.The vertical axis measures average revenue and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of output (number of sandwiches). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 sandwiches, it could go higher.
This curve indicates that if Manny Mustard sells 1 sandwich (at $5.20 per sandwich), then average revenue is $5.20 per sandwich. Alternatively, if he sells 10 sandwiches (at $4.75 per sandwich), then average revenue in is $4.75 per sandwich.
For Manny Mustard the average revenue curve is also the demand curve. The curve is negatively sloped, meaning that larger quantities of output result in less average revenue.
Although this average revenue curve, and preceding table of average revenue numbers, is based on the production activity of Manny Mustard, a well-known monopolistically competitive firm, they apply to any firm with market control. Monopoly and oligopoly firms that also face negatively-sloped demand curves generate comparable average revenues.
AVERAGE REVENUE, MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].


