
|
|
PACKAGING: The container and graphic design variable in the marketing mix, (sometimes included in the product). Changes in product distribution and government regulations in contents identification have made the packaging variable a very important component in the organizationŐs marketing strategy. Packaging completes the marketing process by giving the consumer vital information just prior to making the final buy decision.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           COMPLEMENT-IN-CONSUMPTION: One of two (or more) goods that provide satisfaction of a want or need when consumed together. A complement-in-consumption is one of two alternatives falling within the other prices determinant of demand. The other is a substitute-in-consumption. An increase in the price of one complement good causes a decrease in demand for the other. A complement-in-consumption has a negative cross elasticity of demand. Complements-in-consumption are two or more goods that satisfy wants or needs when consumed jointly. Satisfaction is greater when both goods are consumed together than when they are consumed separately. Buying and consuming either good by itself is not quite as satisfying as both goods combined. In many cases, if both complement goods cannot be consumed, then neither will be purchased. Buy both, or buy neither. The need for food can be satisfied by consuming a hamburger and french fries. The need for transportation can be satisfied by buying a sport utility vehicle and gasoline. The desire to play golf can be satisfied by purchasing golf clubs and golf balls. Satisfaction is less if only one of each pair is consumed. The price of a complement-in-consumption is part of the other prices demand determinant. A change in the price of a complement-in-consumption causes a change in demand and a shift of the demand curve. An increase in the price of one complement good causes a decrease in demand for the other. A decrease in the price of one complement good causes an increase in demand for the other. Shifting the Demand CurveTo illustrate this process consider two bits of complementary sporting equipment--golf clubs and golf balls. While can be used in its own right, when consumed together they enable a satisfying round of golf. Complement-in-Consumption
Golf Balls | 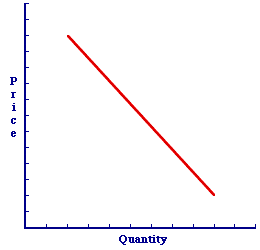
|
How is the demand for golf balls affected if the price of golf clubs should change?- A Higher Price: Suppose the price of golf clubs increases. Golf-playing consumers making a recreational decision will undoubtedly react according to the law of demand and decrease the quantity demanded of golf clubs. However, when they purchase fewer golf clubs, then are also inclined to want and need less golf balls. The result is a decrease in the demand for golf balls and a leftward shift of the demand curve. Click the [Price Increase] button to demonstrate.
- A Lower Price: Suppose the price of golf clubs decreases. Golf-playing consumers will also react according to the law of demand, but in this case they increase the quantity demanded of golf clubs. And as they purchase more golf clubs, then are also inclined to want and need more golf balls. The result is an increase in the demand for golf balls and a rightward shift of the demand curve. Click the [Price Decrease] button to demonstrate.
Cross ElasticityClassifying a good as a complement-in-consumption is accomplished in a precise manner using the cross elasticity of demand. The cross elasticity of demand is the relative response of the demand for one good to changes in the price of another good. More specifically, it is the percentage change in the demand of one good due to a percentage change in the rice of another good. A complement-in-consumption is then one with a cross elasticity that is negative, or less than zero. In comparison, an substitute-in-consumption has a positive, or greater than zero, cross elasticity.

Recommended Citation:COMPLEMENT-IN-CONSUMPTION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 9, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
PURPLE SMARPHIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time going from convenience store to convenience store seeking to buy either a birthday gift for your grandmother or a T-shirt commemorating yesterday. Be on the lookout for the last item on a shelf.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
A half gallon milk jug holds about $50 in pennies.
|

|
|
"All labor that uplifts humanity has dignity and importance and should be undertaken with painstaking excellence. " -- Martin Luther King Jr., civil rights leader
|

|
AAT
Association of Accounting Technicians
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


