
|
|
AGGREGATE MARKET EQUILIBRIUM: The state of equilibrium that exists in the aggregate market when real aggregate expenditures are equal to real production with no imbalances to induce changes in the price level or real production. In other words, the opposing forces of aggregate demand (the buyers) and aggregate supply (the sellers) exactly offset each other. The four macroeconomic sector (household, business, government, and foreign) buyers purchase all of the real production that they seek at the existing price level and business-sector producers sell all of the real production that they have at the existing price level. The aggregate market equilibrium actually comes in two forms: (1) long-run equilibrium, in which all three aggregated markets (product, financial, and resource) are in equilibrium and (2) short-run equilibrium, in which the product and financial markets are in equilibrium, but the resource markets are not.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           RECESSIONARY GAP, KEYNESIAN MODEL: The difference between equilibrium aggregate production achieved in the Keynesian model and full-employment aggregate production that occurs when equilibrium aggregate production is less than full-employment aggregate production. A recessionary gap, also termed a contractionary gap, is associated with a business-cycle contraction. The prescribed Keynesian remedy for a recessionary gap is expansionary fiscal policy. This is one of two alternative output gaps that can occur when equilibrium generates production that differs from full employment. The other is an inflationary gap. A recessionary gap',500,400)">recessionary gap arises in the Keynesian model of the macroeconomy when the equilibrium level of aggregate production falls short of what could be produced at full employment. This represents the condition that arises when the economy is in a business-cycle contraction or recession. Graphically, a recessionary gap is illustrated by the Keynesian cross if equilibrium aggregate production is to the left of full-employment aggregate production.Keynesian Cross Equilibrium| Equilibrium | 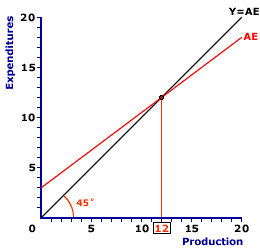 |
The exhibit to the right is a graphical representation of the basic Keynesian model, commonly termed the Keynesian cross. The "cross" term refers to the intersection between two lines, the red AE line and the black Y=AE line.The vertical axis measures expenditures, specifically aggregate expenditures. The horizontal axis measures production, specifically aggregate production or gross domestic product. This exhibit indicates activity in the macroeconomic product markets, or the aggregate product market. The intersection of the 45-degree line and AE line, which is $12 trillion in this exhibit, is equilibrium. At $12 trillion the aggregate expenditures on production is equal to aggregate production. All four sectors are able to purchase all of the output they want and all output produced is purchased by one of the four sectors. There is neither a surplus nor a shortage of aggregate production. But does this level of aggregate production achieve full employment? Full Employment| Full Employment | 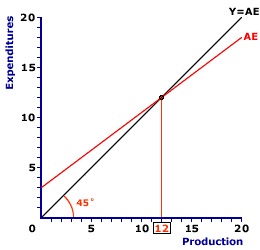
|
An important bit of analysis undertaken using the Keynesian model is the relation between equilibrium and full employment. Should equilibrium aggregate production not match the level of aggregate production generated at full employment, two gaps can arise--recessionary gap and inflationary gap.While we know the equilibrium level of aggregate production from the Keynesian cross analysis above, we also need to know the full-employment level of aggregate production. The relation between the two indicates which of the gaps, if either, might exist. To reveal the full-employment level of aggregate production click the [Full Employment] button in the exhibit to the right. In this particular example, full employment results with $15 trillion of aggregate production, which is greater than the $12 trillion equilibrium level of aggregate production. The relation between equilibrium and full-employment aggregate production means the economy has a recessionary gap. To highlight the recessionary gap in this exhibit, click the [Recessionary Gap] button. The resulting recessionary gap is $3 trillion of aggregate production. In other words, aggregate production needs to increase by $3 trillion to eliminate this gap. This is termed a recessionary gap because it arises during a business-cycle contraction or recession in which unemployment is the more pressing problem facing the macroeconomy. Note that this analysis indicates that the $12 trillion equilibrium can be at a level of aggregate production that is less than full employment. And because $12 trillion is EQUILIBRIUM it persists once reached. There is no mechanism within the Keynesian model that automatically moves aggregate production to the full employment level. As such, an outside force must intervene to achieve full employment. The recommended Keynesian remedy is stabilization policies, especially fiscal policy. In particular, a recessionary gap is closed through the use of expansionary fiscal policy. Expansionary Fiscal PolicyExpansionary fiscal policy is an increase in government spending and/or a decrease in taxes designed to avoid or correct the problems associated with a business-cycle contraction.Either action causes an increase or upward shift of the aggregate expenditures line. If the correct vertical shift is achieved, then the Keynesian model can achieve equilibrium at the $15 trillion full-employment level of aggregate production. Such a result would close the recessionary gap, eliminate the business-cycle contraction, and reduce the level of unemployment. Inflationary GapA recessionary gap is one of two alternatives that can arise if equilibrium aggregate production does not match full-employment aggregate production. The other is an inflationary gap. An inflationary gap results if equilibrium production is greater than full-employment production. This is the sort of gap that tends to occur during a business-cycle expansion and creates a situation in which inflationary pressure arises, meaning inflation is the more pressing problem facing the macroeconomy.

Recommended Citation:RECESSIONARY GAP, KEYNESIAN MODEL, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
PINK FADFLY
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time calling an endless list of 800 numbers wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for high interest rates.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The wealthy industrialist, Andrew Carnegie, was once removed from a London tram because he lacked the money needed for the fare.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
PDI
Personal Disposable Income
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


