
|
|
PERSONAL INCOME AND DISPOSABLE INCOME: Personal income (PI) is the total income received by the members of the domestic household sector, which may or may not be earned from productive activities during a given period of time, usually one year. Disposable income (DI) is the total income that can be used by the household sector for either consumption or saving during a given period of time, usually one year. Disposable income is after-tax income that is officially calculated as the difference between personal income and personal tax and nontax payments. In the numbers game, personal tax and nontax payments are about 15% of personal income, which makes disposable personal income about 85% of personal income.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION, DEMAND: The demand curve for the output produced by a monopolistically competitive firm is relatively elastic. The firm can sell a wide range of output within a relatively narrow range of prices. As a price maker, the firm has some ability (not much, but some) to control price. The demand curve is negatively sloped, but relatively elastic, because each firm produces a slightly differentiated product, but faces competition from a large number of very, very close substitutes. A monopolistically competitive industry is comprised of a large number of relatively small firms that sell similar but not identical products. Each firm is small relative to the overall size of the market such that it has some market control, but not much. In other words, it can sell a wide range of output at a narrow range of prices. This translates into a relatively elastic demand curve. But it also means that price (and average revenue) are greater than marginal revenue.Manny Mustard's SandwichesTake, for example, Manny Mustard's House of Sandwich and his specialty the Deluxe Club Sandwich. Manny's restaurant is one of 2,000 that dot the urban landscape of Shady Valley, all of which produce potential substitutes for the Deluxe Club Sandwich. Some, like Debbie Duncan's Deli Delight, also offer club sandwiches for sale. Others, like Ships Ahoy Seafood Safari and Waldo's TexMex Taco World, sell non-sandwich meals such as fish and chips or tacos.In this case, the price that Manny Mustard charges and receives for his sandwiches falls within a narrow range of prices. A Debbie Duncan's Deli Delight variety of club sandwich sells for $5.50. A comparable meal at the Ships Ahoy Seafood Safari runs a hungry patron $6.50. Manny remains competitive if the price of his Deluxe Club Sandwich falls around this range. Maybe a little more, maybe a little less. If Manny's price is TOO HIGH, his customers switch to Debbie Duncan's. And if Manny lowers his price TOO MUCH, he can be overwhelmed by TOO MANY buyers. Relatively Elastic DemandDemand Curve,
Monopolistic Competition | 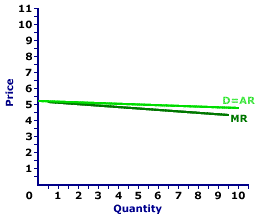 |
The four characteristics of monopolistic competition mean that a monopolistically competitive firm faces a relatively, but not perfectly, elastic demand curve, such as the one labeled D=AR and displayed in the exhibit to the right. Each firm in a monopolistically competitive market can sell a wide range of output within a relatively narrow range of prices.Demand is relatively elastic in monopolistic competition because each firm faces competition from a large number of very, very close substitutes. However, demand is not perfectly elastic (as in perfect competition) because the output of each firm is slightly different from that of other firms. Monopolistically competitive goods are close substitutes, but not perfect substitutes. In the exhibit to the right, the monopolistically competitive firm can sell up to 10 units of output within the range of $4.50 to $5.50. In particular, should the price go higher than $5.50, the quantity demanded drops to zero. Average, But Not Marginal RevenueA monopolistically competitive firm is a price maker, with some degree of control over price. Once again, unlike perfect competition, a monopolistically competitive firm has the ability to raise or lower the price a little, not much, but a little. And like monopoly, the price received by a monopolistically competitive firm (which is also the firm's average revenue) is greater than its marginal revenue. This demand curve is also the average revenue curve facing Manny Mustard for selling his sandwiches, which is why it is labeled D = AR. Average revenue is the per unit revenue received for selling sandwiches. If Manny Mustard sells 5 sandwiches for $5.00 each, his total revenue is $25. His per sandwich revenue for these 5 sandwiches is then $5.00, which is also the price. However, because Manny is a price maker with some degree of market control price is not equal to marginal revenue. For example, 5 sandwiches correspond to a $5 price but the marginal revenue for the fifth sandwich is $4.80, less than price. In the exhibit above, the marginal revenue curve (MR) lies below the demand/average revenue curve (D = AR). Even though marginal revenue is less than price, because demand is relatively elastic, the difference tends to be relatively small.

Recommended Citation:MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION, DEMAND, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLACK DISMALAPOD
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing about a thrift store seeking to buy either a genuine fake plastic Tiffany lamp or a microwave over that won't burn your popcorn. Be on the lookout for small children selling products door-to-door.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Ragnar Frisch and Jan Tinbergen were the 1st Nobel Prize winners in Economics in 1969.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
SPSS
Statistical Product and Service Solutions, Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (software)
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


