
|
|
ASSOCIATION OF SOUTHEAST ASIAN NATIONS: The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a subregional organization established in 1967 in Bangkok by the five original Member Countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. Brunei Darussalam joined in 1984, Vietnam in 1995, Laos and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999. The aims and purposes of the Association are to accelerate the economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region and to promote regional peace and stability through abiding respect for justice and the rule of law.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MONEY SUPPLY, AGGREGATE DEMAND DETERMINANT: One of several specific aggregate demand determinants assumed constant when the aggregate demand curve is constructed, and that shifts the aggregate demand curve when it changes. An increase in the money supply causes an increase (rightward shift) of the aggregate curve. A decrease in the money supply causes a decrease (leftward shift) of the aggregate curve. Other notable aggregate demand determinants include interest rates, inflationary expectations, and the federal deficit. A key function of the Federal government is controlling the total amount of money circulating about the economy. Money is what the public uses to buy real production and to undertake the four aggregate expenditures--consumption expenditures, investment expenditures, government purchases, and net exports.- With more money, aggregate expenditures are greater.
- With less money, aggregate expenditures are lower.
As such, changes in the money supply induces changes in aggregate demand. An increase in the money supply increases aggregate demand and a decrease in the money supply decreases aggregate demand.| Shifting the Curve | 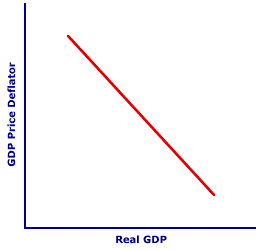 |
Consider a regular, run-of-the-mill aggregate demand curve such as the one displayed here. Like all aggregate demand curves, this one is constructed based on several ceteris paribus aggregate demand determinants, such as the size of the money supply. The key question is: What happens to the aggregate demand curve if the money supply changes?More MoneySuppose, for example, that the Federal Reserve System decides to undertake expansionary monetary policy. Fearing an impending recession on the business-cycle horizon, it decides to expand the money supply. With extra money circulating about the economy, the purchasing power of all four sectors--household, business, government, and foreign--is enhanced. Everyone is willing and able to buy more real production--at the existing price level. Consumption expenditures, investment expenditures, government purchases, even net exports, all increase, resulting in an increase in aggregate demand.To see how an increase in the money supply affects the aggregate demand curve, click the [More Money] button. The boost in the money supply triggers an increase in aggregate demand, which is a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve. Less MoneyAlternatively, the Federal Reserve System could decide to implement contractionary monetary policy. Fearing the onset of higher inflation, the "Fed" might decide to reduce the money supply. With less money circulating about the economy, the purchasing power of all four sectors--household, business, government, and foreign--is restricted. Everyone is willing and able to buy less real production--at the existing price level. Consumption expenditures, investment expenditures, government purchases, even net exports, all decrease, resulting in a decrease in aggregate demand.To see how a decrease in the money supply affects the aggregate demand curve, click the [Less Money] button. The drop in the money supply triggers a decrease in aggregate demand, which is a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve What Does It Mean?The importance of the money supply as an aggregate demand determinant is critical to the study of macroeconomics, especially monetary policy designed to stabilize business cycles. A frequently recommended, and often pursued, solution to business-cycle contractions is expansionary monetary policy, an increase in the money supply. Alternatively, a solution to business-cycle expansions that causes inflation is contractionary monetary policy, a decrease in the money supply.When these policies are implemented, the aggregate demand curve shifts, which then induces changes in production, unemployment, and the price level. Ch...Ch...ChangesDo not confuse changes in the money supply, as an aggregate demand determinant, with the real-balance effect. While both involve the money supply, they are distinct phenomena. The real-balance effect occurs because changes in the price level cause changes in aggregate expenditures and movements along the aggregate demand curve. The real-balance effect operates because A CHANGE IN THE PRICE LEVEL causes a change the purchasing power of A GIVEN MONEY SUPPLY.By way of contrast, money supply as an aggregate demand determinant causes changes in aggregate demand and shifts of the aggregate demand curve. This determinant operates because of a change in the money supply. In comparison with the real-balance effect, the aggregate demand curve shifts because A CHANGE IN THE MONEY SUPPLY causes a change in purchasing power at A GIVEN PRICE LEVEL.

Recommended Citation:MONEY SUPPLY, AGGREGATE DEMAND DETERMINANT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the downtown area trying to buy either shoe laces for your snow boots or a rim for your spare tire. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The average bank teller loses about $250 every year.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
FTC
Federal Trade Commission
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


