
|
|
MACRO GOALS: The three goals of a mixed economy that are most relevant to the study of macroeconomics are full employment, stability, and economic growth. Full employment is the condition in which all of the economy's available resources are engaged in the production of goods and services. Stability is the condition in which the economy avoids large changes in production, employment, and especially prices. Economic growth is the condition in which the economy's production possibilities are expanding over time.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           PREFERENCES CHANGE, UTILITY ANALYSIS: A disruption of consumer equilibrium identified with utility analysis caused by changes in the preferences for a good, which likely results in a change in the quantities of the goods consumed. The change in preferences alters the marginal utility-price ratio and forces a reevaluation of the rule of consumer equilibrium. Utility analysis can be used to illustrate how a change in the preferences for a good alters the consumer equilibrium combination of goods consumed. With an increase or decrease in preferences, a consumer is more or less willing to purchase a good. This particular utility analysis provides insight into the buyers' preferences demand determinant. A Review of Consumer Equilibrium| Pretzels and Sundaes | 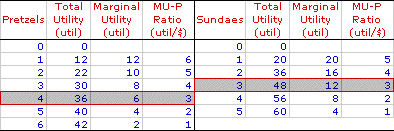 |
First, a review of consumer equilibrium is in order. A Change Sundae PreferencesThe main point of analysis is to pose the question: What happens if there is a change in the preferences for one of the goods? In particular, suppose that Duncan's preferences for hot fudge sundaes increases. How might the consumer equilibrium purchase of pretzels and hot fudge sundaes change?| Pretzels and Sundaes |  |
This change in preferences is reflected by a change in the total utility and marginal utility derived from sundae consumption. Click the [New Preferences] button to illustrated this change. The new numbers indicate that Duncan likes hot fudge sundaes substantially more than before the change.For example, prior to the change, Duncan receives a total of 48 utils for consuming 3 hot fudge sundaes. After the change he receives a total of 84 utils for the same quantity. Moreover, the marginal utility of the third sundae is 12 utils before the preference change and 24 utils after the change. This is just the sort of change that is bound to disrupt consumer equilibrium and throw the rule of consumer equilibrium out of balance. The key to identifying the imbalance and determining the new consumer equilibrium is the marginal utility-price ratio. Because the hot fudge sundae marginal utilities change, the marginal utility-price ratios also change. The new ratios, given the existing $4 price, are also presented in the table. Note that for each hot fudge sundae, Duncan now receives a greater level of satisfaction per dollar spent. This new set of marginal utility-price ratios reveals that the original purchase of 3 sundaes generates 6 utils per dollar, compared to the initial ratio of 3 utils per dollar. Moreover, this new ratio confirms that the rule of consumer equilibrium is out of balance. The fourth pretzel generates 3 utils per dollar, but the third sundae generates 6 utils per dollar. Because Duncan receives a greater amount of satisfaction per dollar spent on sundaes, it seems reasonable for him to purchase more sundaes, fewer pretzels, or a combination of the two. Of course, given that his income remains at $20, if he chooses to buy more sundaes, he must necessarily purchase fewer pretzels. - Suppose Duncan opts for a fourth sundae. If so, his total expenditure rises to $24, and the marginal utility-price ratio for sundaes falls to 5 utils per dollar. While this moves him closer to consumer equilibrium, the rule of consumer equilibrium remains out of balance. His sundae marginal utility-price ratio (5 utils per dollar) is still greater than his pretzel marginal utility-price ratio (3 utils per dollar). Even worse, the $24 expenditure exceeds his $20 budget.
- Duncan can reduce his total expenditure by the $4 needed to achieve his $20 budget if he consumes 2 fewer pretzels. In so doing, the marginal utility of pretzels increases, working the law of diminishing marginal utility in reverse, which then causes the pretzel marginal utility-price ratio to rise. If Duncan decides to consume 2 pretzels rather than 4, his total expenditure declines to $20 and the pretzel marginal utility-price ratio rises to 5 utils per dollar.
This combination appears to be a workable solution. The purchase of 4 hot fudge sundaes and 2 pretzels achieves consumer equilibrium, given the new hot fudge sundae preferences. This combination satisfies the rule of consumer equilibrium and maximizes the utility achieved with his $20 budget. Click the [New Equilibrium] button to highlight this combination.What can be concluded from the analysis of this change in preferences? Most importantly, Duncan consumes more sundaes, 4 versus 3. But this is just what would be expected if Duncan likes sundaes more.

Recommended Citation:PREFERENCES CHANGE, UTILITY ANALYSIS, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 1, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time waiting for visits from door-to-door solicitors looking to buy either a coffee cup commemorating the first day of winter or a video game player. Be on the lookout for malfunctioning pocket calculators.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The 1909 Lincoln penny was the first U.S. coin with the likeness of a U.S. President.
|

|
|
"Experience keeps a dear school, but fools will learn in no other. " -- Benjamin Franklin
|

|
BST
Bulk Supply Tariff
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


