
|
|
ANNUAL: A standard 12-month period, or one year, used for reporting economic and financial data. Gross Domestic Product and related measures are noted economic data released annually. Many businesses also provide annual financial reports. Another standard reporting period is the quarter.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           EXPORTS LINE: A graphical depiction of the relation between exports sold to the foreign sector and the economy's aggregate level of income or production. This relation is most important for deriving the net exports line, which plays a minor, but growing role in the study of Keynesian economics. An exports line is horizontal which indicates that exports are totally autonomous, with no induced component. The aggregate expenditures line used in Keynesian economics is derived by adding or stacking the net exports line, derived as the difference between the exports line and imports line, onto the consumption line, after adding investment expenditures and government purchases. The exports line shows the relation between exports of domestic production purchased by the foreign sector and aggregate income or production. The income and production measures most commonly used are national income and gross domestic product. The purpose of the exports line is to graphically illustrate the exports-income relation for the foreign sector, which is then used to derive the net exports line by vertically subtracting the imports line, after which it is then integrated into the aggregate expenditures line used in Keynesian economics.Net exports are the difference between exports and imports, or exports minus imports. Exports are purchases of domestic production by the foreign sector and imports are purchases of foreign production by the domestic economy. While imports are induced by the level of domestic income and production, exports are totally autonomous. Reflecting this, the exports line is horizontal, with a zero slope. There are no induced exports. The vertical intercept, or Y-intercept, of the exports line reflects autonomous exports. | Exports Line | 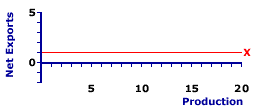 |
The horizontal red line, labeled X in the exhibit to the right, indicates a typical exports line. Line any straight line, this exports line is characterized by two key parameters, intercept and slope. The intercept indicates autonomous exports and the slope indicates the degree of induced exports, if any actually existed.Identifying numbers for these two parameters for this particular line indicates that the intercept is $1 trillion, meaning autonomous exports is $1, and the slope is 0, meaning a $1 increase in domestic income or production induces a $0 decrease in exports. A zero slope means exports are autonomous and equal to $1 trillion for every level of domestic income and production.

Recommended Citation:EXPORTS LINE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
PINK FADFLY
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time calling an endless list of 800 numbers wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for high interest rates.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
In the Middle Ages, pepper was used for bartering, and it was often more valuable and stable in value than gold.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
SIB
Securities and Investment Board
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


