
|
|
EFFECTIVE DEMAND: The notion that the actual demand for aggregate output in the macroeconomy is based on the actual income or other existing economic conditions and not on income and conditions existing in equilibrium. The idea of effective demand plays a key role in Keynesian economics and how the macroeconomy can have extended periods of unemployment. Effective demand is in direct contrast to the view underlying classical economics that demand is that existing in equilibrium.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL PRODUCT AND MARGINAL PRODUCT: A mathematical connection between marginal product and total product stating that marginal product IS the slope of the total product curve. If the total product curve has a positive slope (that is, is upward sloping), then marginal product is positive. If the total product curve has a negative slope (downward sloping), then marginal product is negative. If the total product curve has a zero slope (horizontal), then marginal product is zero. The relation between total product and marginal product is one of several that reflect the general relation between a total and the corresponding marginal. There general relation is this: A marginal is the slope of the total curve. Marginal is another term for slope.The general relation between total and marginal surfaces throughout the study of economics, especially utility (total utility and marginal utility), cost (total cost and marginal cost), revenue (total revenue and marginal revenue), and consumption (consumption expenditures and marginal propensity to consume). Making Tacos| Total and Marginal Product | 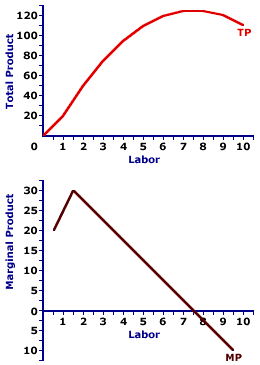 |
This two-paneled graph for the hourly production of Super Deluxe TexMex Gargantuan Tacos (with sour cream and jalapeno peppers) that visually illustrates the connection between total product and marginal product.- For the first few quantities of the variable input (the number of workers), total product in the top panel is positive AND the slope of the total product curve increases, it becomes steeper. This corresponds with a positive and increasing marginal product in the bottom panel.
- For the next several quantities of the variable input, the slope of the total product curve flattens out, although positive, the slope decreases. This corresponds to a decreasing marginal product in the bottom panel.
- For the last few quantities of the variable input, the slope of the total product curve in the top panel is negative. This corresponds with a negative marginal product in the bottom panel.
The Law of Diminishing Marginal ReturnsThe prime conclusion to drawn from this is the key role played by the law of diminishing marginal returns in the slope of both the marginal product curve and the total product curve. The "hump shape" of the marginal product curve is a direct reflection of first increasing marginal returns, as marginal product rises to a peak, then decreasing marginal returns and the onset of the law of diminishing marginal returns as marginal product falls.However, because the marginal product curve is essentially a plot of the slope of the total product curve, the shape of the total product curve also reflects the law of diminishing marginal returns. The increasingly steep slope of the total product curve for small quantities of the variable input is due to increasing marginal returns. Then with the onset of the law of diminishing marginal returns causes the total product curve to flatten out and subsequently turn down.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL PRODUCT AND MARGINAL PRODUCT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 1, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time waiting for visits from door-to-door solicitors looking to buy either a coffee cup commemorating the first day of winter or a video game player. Be on the lookout for malfunctioning pocket calculators.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The penny is the only coin minted by the U.S. government in which the "face" on the head looks to the right. All others face left.
|

|
|
"Experience keeps a dear school, but fools will learn in no other. " -- Benjamin Franklin
|

|
AS
Aggregate Supply
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


