
|
|
INCREASING RETURNS TO SCALE: A given proportionate increase in all resources in the long run results in a proportionately greater increase in production. Increasing returns to scale exists if a firm increases ALL resources -- labor, capital, and other inputs -- by 10%, and output increases by more than 10%. You might want to compare decreasing returns to scale and constant returns to scale.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARKET-CLEARING PRICE: The price that exists when a market is clear of shortage and surplus, or is in equilibrium. Market-clearing price is a common, non-technical term for equilibrium price. In a market graph, the market-clearing price is found at the intersection of the demand curve and the supply curve. Market-clearing price is the price that achieves a market balance. Because quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal at the market-clearing price, there is no shortage nor surplus in the market, which means that neither buyers nor sellers are inclined to change the price, which is the primary condition for equilibrium.Moreover, because the market-clearing price also simultaneously equates the demand price and supply price, the market equilibrium generates an efficient allocation of resources (presuming competition and no market failures). Clearing the Market| Market-clearing Price | 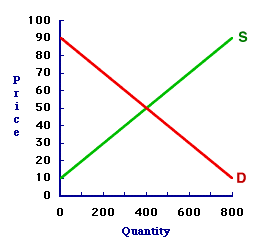 |
The market model displayed in the exhibit to the right can be used to identify the market-clearing price. This particular model represents the market for 8-track tapes, which are filled with the works of classic performers such as The Carpenters and Englebert Humperdink. The buyers and sellers happen to be folks attending the 88th Annual Trackmania 8-Track Tape Collectors Convention at the Shady Valley Exposition Center.The market-clearing price achieves a balance in the market, which is equality between quantity demanded and quantity supplied. In other words, it clears the market of any shortage or surplus. The only price that accomplishes this task is at the intersection of the demand curve and supply curve. This intersection point, and the price that achieves it, can be identified by clicking the [Market-Clearing Price] button in the exhibit. Doing so reveals a market-clearing price of 50 cents. At this price, the demand curve and supply curve intersect. The quantity demanded is 400 tapes and the quantity supplied is 400 tapes. The quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. The buyers can buy all that they want, so there is no shortage. The sellers can sell all that they want, so there is no surplus. Neither buyers nor sellers are motivated to change the price. The forces of demand and supply are in balance. This is the ONLY price that achieves a balance between these two quantities. Best of all, because this is equilibrium, the market-clearing price of 50 cents will not change and the equilibrium quantity of 400 tapes will not change unless or until an external force intervenes.

Recommended Citation:MARKET-CLEARING PRICE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: June 30, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GRAY SKITTERY
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time strolling around a discount warehouse buying club seeking to buy either a flower arrangement with a lot of roses for your grandmother or a wall poster commemorating the first day of winter. Be on the lookout for cardboard boxes.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
General Electric is the only stock from the original 1896 Dow Jones Industrial Average remaining in the current index.
|

|
|
"I learned about the strength you can get from a close family life. I learned to keep going, even in bad times. I learned not to despair, even when my world was falling apart. I learned that there are no free lunches. And I learned the value of hard work. " -- Lee Iacocca
|

|
L/C
Letter of Credit
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


