
|
|
OLIGOPOLY, CONCENTRATION: Oligopoly is a market structure that contains a small number of relatively large firms, meaning oligopoly markets tend to be concentrated. A small number of large firms account for a majority of total output. Concentration unto itself is not necessarily bad, but it often leads to inefficient behavior, such as collusion and nonprice competition. Concentration is measured in three ways--market share, concentration ratio, Herfindahl index.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           CLASSICAL AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE: An aggregate supply curve--a graphical representation of the relation between real production and the price level--that reflects the basic principles of classical economics. The classical aggregate supply curve is vertical at the full-employment level of real production indicating that the quantity of aggregate production is independent of the price level. An alternative is the Keynesian aggregate supply curve. An aggregate supply curve is a graphical representation of the relation between real production and the price level. Classical economics implies that the full-employment level of real production is maintained regardless of the price level, which creates a vertical, or perfectly elastic, aggregate supply curve. This relation results due to flexible prices, which ensure that resources markets maintain equilibrium balance at full employment. Should the price level rise or fall, wages and resource prices adjust to ensure that quantity demanded equals quantity supplied in resource markets.| Classical AS Curve | 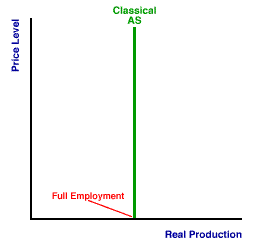 |
The exhibit to the right illustrates a classical aggregate supply (AS) curve. The obvious characteristic is that the curve is actually a vertical line. The line is vertical at the full-employment level of real production. Should the price level rise or fall, the economy moves up and down along the curve and real production remains unchanged.The full-employment level of real production corresponds to the natural unemployment rate, also termed the non-accelerating inflation unemployment rate. The measured unemployment rate is not necessarily zero. This rate includes both frictional unemployment and structural unemployment and results if the quantity of labor demanded is equal to the quantity of labor supplied. The classical aggregate supply curve looks a great deal like the long-run aggregate supply curve. Both are vertical at the full-employment level of real production. Both indicate that real production is unaffected by changes in the price level. The reason for the similarity is that the long-run aggregate supply curve is the modern embodiment of the principles of classical economics. For the classical aggregate supply curve, changes in the price level results in changes in wages and resource prices that ensure equality between quantity demanded equals quantity supplied in resource markets. For the long-run aggregate supply curve, changes in the price level results in changes in wages and resource prices that ensure equality between quantity demanded equals quantity supplied in resource markets--in the long run.

Recommended Citation:CLASSICAL AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: June 30, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing through a long list of dot com websites wanting to buy either a Boston Red Sox baseball cap or a square lamp shade with frills along the bottom. Be on the lookout for pencil sharpeners with an attitude.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
A U.S. dime has 118 groves around its edge, one fewer than a U.S. quarter.
|

|
|
"I learned about the strength you can get from a close family life. I learned to keep going, even in bad times. I learned not to despair, even when my world was falling apart. I learned that there are no free lunches. And I learned the value of hard work. " -- Lee Iacocca
|

|
DW
Durbin-Watson
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


