
|
|
DEMAND DECREASE AND SUPPLY INCREASE: A simultaneous decrease in the willingness and ability of buyers to purchase a good at the existing price, illustrated by a leftward shift of the demand curve, and an increase in the willingness and ability of sellers to sell a good at the existing price, illustrated by a rightward shift of the supply curve. When combined, both shifts result in an indeterminant change in equilibrium quantity and a decrease in equilibrium price.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           FACTOR SUPPLY DETERMINANTS: Ceteris paribus influences, other than factor price, that shift the factor supply fall into three general categories: (1) market supply determinants, (2) market demand determinants, and (3) mobility. Comparable to any determinant, those falling into these three categories cause the factor supply curve to shift to a new location. An increase in factor supply is a rightward shift of the factor supply curve and a decrease in factor supply is a leftward shift. Factor supply determinants are ceteris paribus variables held constant when a factor supply curve is constructed. As they change, the factor supply curve shifts. These determinants are as diverse as the inputs included under the heading of factor supply. In particular, factor inputs include both produced goods as well as humans. The determinants underlying the factor supply of produced goods, such as capital, are like those of market supply. The determinants underlying the factor supply of human inputs are related to those of market demand. Factor supply determinants fall into three general categories: (1) market supply determinants, (2) market demand determinants, and (3) mobility. Making Duct TapeConsider the production activity of Mona Mallard Duct Tape Company. Mona Mallard uses several different types of resources in the production of duct tape. Labor services are supplied by human beings such as Chip Merthington and Judy Johansen. A wide range of capital services are also used, including the factory building, adhesive application machines, and delivery trucks. Land provides space for the factor building as well as the raw materials that become the duct tape. Mona Mallard provides the entrepreneurship.Each of these inputs comes to Mona Mallard through a factor supply relation. The quantity supplied largely depends on the factor price of each resource. However, like any other supply relation, price is not the only influence. The diversity found in the factors used for production create an equal diversity of factor supply determinants. In particular, most of the ten standard market demand and supply determinants show up as determinants of factor supply. This occurs because some factor supplies, especially for capital goods and land materials, work much like market supply, while other factors, most notably labor and entrepreneurship, involve human consumption choices comparable to those underlying market demand. How They Work| Duct Tape Employment | 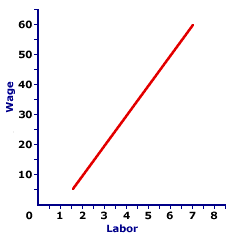 |
The accompanying diagram displays the factor supply curve for duct tape employment in the Shady Valley area. Because factor supply for duct-tape workers is based on the opportunity cost of foregone activities this curve is positively sloped. Workers are willing to supply a larger quantity of labor if they receive a higher wage. This higher wage compensates for the increasing opportunity cost.Consider how an increase in factor supply and a decrease in factor supply are illustrated in this diagram. Click the [Increase] button to display an increase in factor supply. Obviously the factor supply curve shifts rightward. At each wage, at every wage, more workers are willing and able to supply their services. Now click the [Decrease] button to display a decrease in factor supply. Here the factor supply curve shifts leftward. At each wage, at every wage, fewer workers are willing and able to supply their services. From Market SupplyIn that factor supply involves produced inputs like standard market supply, the five standard supply determinants--resource prices, technology, other prices, expectations, and number of sellers--are also important factor supply determinants.- Resource Prices: A change in the prices paid for any input used to produce any of the factors purchased by Mona Mallard affects its factor supply curve. A change in the price of steel used in the production of adhesive application machines affects the factor supply of this resource. A change in the cost of consumer goods purchased by workers also affects the factor supply of labor.
- Technology: Improvements in the technology associated with a factor increase the factor supply. Should the technology of mining quagliminium (a key mineral used to make the sticky adhesive for duct tape) improve, then the factor supply of quagliminium increases.
- Other Prices: Should the prices of other factors that have a substitute or complement relation with the production of the factor input used by Mona Mallard, then the factor supply also changes. Suppose that the price of fork lifts increases. Fork lifts use the same steel that goes into the production of adhesive application machines. As such, the steel is diverted away from adhesive application machines and into fork lift production, causing a decrease in the factor supply of adhesive application machines.
- Expectations: Should resource owners expect higher or lower future factor prices, then they adjust their factor supplies to achieve the highest possible price. If quagliminium suppliers expect higher futures prices, they decrease their current factor supply.
- Number of Sellers: More sellers, mean greater factor supply. An increase in the population of Shady Valley, means that the supply of labor increases.
From Market DemandBecause labor and entrepreneurship have human involvement, three of the five standard demand determinants--income, preferences, and other prices--are also worth noting as factor supply determinants.- Income: Because more labor means less leisure, and leisure is generally a normal good, an increase in income typically decreases the factor supply of labor. If Chip Merthington wins a $10 million lottery, then he is likely to quit his job working for Mona Mallard.
- Preferences: Because workers receive satisfaction from the job itself, should preferences change, so too does the willingness to supply labor. If Judy Johansen grows disgusted with the drudgery of duct tape production, she too might quit her job with Mona Mallard.
- Other Prices: Leisure is the primary alternative to labor. Should the price of leisure change, the willingness to supply labor also changes. As a potential househusband, Ivan Herwig might be inclined to leave the life of an employed duct-tape worker should the rewards of staying at home increase.
MobilityA third set of factor supply determinants falls under the mobility heading. Mobility is the ease with which resources or factors of production can move from one productive activity to another. Two types of mobility are geographic and occupational. - Geographical Mobility: This is the movement of factors from a productive activity in one location to a productive activity in another location. For example, a worker leaves a job in one city and takes a job in another city.
- Occupational Mobility: This is the movement of factors from one type of productive activity to another type of productive activity. For example, a worker leaves a job as an accountant and takes a job as a computer programmer.

Recommended Citation:FACTOR SUPPLY DETERMINANTS, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
PURPLE SMARPHIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time flipping through mail order catalogs trying to buy either a flower arrangement for your aunt or a birthday greeting card for your uncle. Be on the lookout for rusty deck screws.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The earliest known use of paper currency was about 1270 in China during the rule of Kubla Khan.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
LME
London Metal Exchange
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


