
|
|
LOCAL INPUT: An input that has a relatively small geographic market area due to the high cost of transportation. The high transportation cost means it is easier (that is, less expensive) to locate the production activity near the input rather than trying to bring the input to the production activity. Like many things, local inputs are a matter of degree. At the other end of the spectrum lies transferrable inputs. Natural resources of the land, such as soil fertility, weather conditions, mineral deposits, tend to have the greatest local orientation. Labor and many urban public utilities, such as water distribution and sewage disposable, also tend to fall into the local category.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           LONG-RUN AVERAGE COST CURVE, DERIVATION: The long-run average cost curve is the envelope of an infinite number of short-run average total cost curves, with each short-run average total cost curve tangent to, or just touching, the long-run average cost curve at a single point corresponding to a single output quantity. The key to the derivation of the long-run average cost curve is that each short-run average total cost curve is constructed based on a given amount of the fixed input, usually capital. As such, when the quantity of the fixed input changes, the short-run average total cost curve shifts to a new location. The long-run average cost curve can be derived by identifying the factory size (or quantity of capital) that can produce each quantity of output at the lowest short-run average total cost. For example, The Wacky Willy Company has one short-run average total cost curve corresponding to a 10,000 square foot factory, another short-run average total cost curve corresponding to a 10,001 square foot factory, another for a 10,002 square foot factory, etc. Each of these short-run average total cost curves incurs the lowest average total cost for the production of a given quantity of output. The long-run average cost curve is then the combination of all minimum short-run average total cost values.Starting with Five FactoriesThe derivation of a long-run average cost curve can be had using The Wacky Willy Company and the production of Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos (those cute and cuddly armadillos, tarantulas, and scorpions). The diagram below presents five short-run average total cost curves corresponding to five alternative factory sizes that could be used to produce Stuffed Amigos--10,000 square feet, 20,000 square feet, 30,000 square feet, 40,000 square feet, and 50,000 square feet. These five factors reach minimum short-run average total cost at production levels of 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 Stuffed Amigos, respectively.
| Long Run Average Cost | 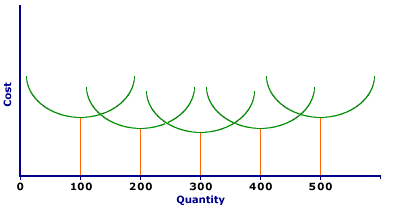 |
In the long run, The Wacky Willy Company can choose either one of these five factory sizes. However, once a factory size is selected, Stuffed Amigos production is confined to the corresponding short-run average cost curve (as well as corresponding short-run average variable cost and short-run marginal cost curves which are not shown) until the quantity of capital is changed in the long run. The prime question facing The Wacky Willy Company is: Which factory size should it select? The answer directly depends on the quantity of Stuffed Amigos it intends to produce. If it plans to produce somewhere around a 100 Stuffed Amigos, then the smallest factory is appropriate. For the production of 100 Stuffed Amigos, the 10,000 square foot factory has lower short-run average total cost than any of the larger factories. Should The Wacky Willy Company try to produce a mere 100 Stuffed Amigos using the second smallest, 20,000 square foot factory, average total cost is substantially higher. To see how high, extend the 100 Stuffed Amigos quantity until intersecting the second smallest short-run average total cost curve. The reason the larger factory has higher average total cost than the smaller one is largely due to fixed cost. The larger factory has more capital and thus higher total fixed cost. As such, average fixed cost is also higher for the production of the relatively small quantity of 100 Stuffed Amigos. If, for example, the total fixed cost of the 10,000 square foot factory is $1,000 per day, the average fixed cost of producing 100 Stuffed Amigos is $10 per Stuffed Amigo. However, the 20,000 square foot factory has higher total fixed cost, say $2,000 per day. This makes average fixed cost $20 per Stuffed Amigo. With higher average fixed cost, average total cost is also higher. Production RangesEach of these five factories can produce Stuffed Amigos at a lower cost than the others over a range of production. The specific ranges are given in the exhibit below. The smallest factory has lower average total cost up to 135 Stuffed Amigos, the quantity at which the short-run average total cost curves for the smallest and second smallest intersect. In the range of 200 Stuffed Amigos (precisely from 135 to 240 Stuffed Amigos) the second smallest factory has lower average total cost than the others. The production ranges for the remaining three factors are 240 to 360, 360 to 465, and anything over 465.
| Production Ranges | 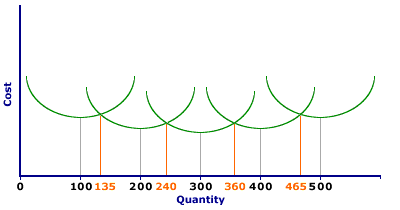
|
If The Wacky Willy Company is faced ONLY with the choice of these three factory sizes, it selects the first if it plans to produce up to 135 Stuffed Amigos, the second if it plans to produce between 135 and 240 Stuffed Amigos, the third if it plans to produce between 240 and 360 Stuffed Amigos, the fourth if it plans to produce between 360 and 465 Stuffed Amigos, and the fifth if it plans to produce more than 465 Stuffed Amigos. The long-run average cost curve for The Wacky Willy Company is therefore the lower portions of each of the short-run average total cost curves that lie below the others. Up to 135 Stuffed Amigos, the long-run average cost curve is the short-run average total cost curve for the 10,000 square foot factory. However, between 135 and 240 Stuffed Amigos, the short-run average total cost curve for the 20,000 square foot factory is the long-run average total cost curve. For production between 240 and 360 Stuffed Amigos, the short-run average total cost curve for the middle factory is the long-run average total cost curve. Click the [Lowest Cost Envelope] button to highlight those segments of the five short-run average total cost curves that make up the long-run average cost curve. Adding Another FourIf The Wacky Willy Company faces only five factor sizes, this analysis ends right here. However, in reality it is likely to have other options. To add four more factor sizes to the original set of five presented in the following exhibit, click the [More Factories] button.
| Four More Factories | 
|
The four additional factories reach their minimum values at 150, 250, 350, and 450 Stuffed Amigos. The inclusion of these additional factories also reduces the production ranges in which the original five factories have lower short-run average total cost than the others.The inclusion of other factories reduces those production ranges even more, until eventually the production range for each factory is a single quantity of output. The combination of the short-run average total cost values corresponding to each "one quantity" production range is then the long run average cost curve. To demonstrate the long-run average cost curve for The Wacky Willy Company click the [Long Run Average Cost] button.

Recommended Citation:LONG-RUN AVERAGE COST CURVE, DERIVATION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
YELLOW CHIPPEROON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads trying to buy either a T-shirt commemorating the 2000 Olympics or a genuine fake plastic Tiffany lamp. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from former employers.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Two and a half gallons of oil are needed to produce one automobile tire.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
DPI
Disposable Personal Income
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


