
|
|
LONG-RUN EQUILIBRIUM, MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION: Relative freedom of entry and exit ensures that, in the long run, every firm in a monopolistically competitive industry earns exactly a normal profit, receiving neither an economic profit, nor incurring an economic loss. This result is achieved because entry and exit affects the market supply curve, which affects the overall market price, each firm's demand curve, and the range or prices it can charge. Each firm's demand curve adjusts until the profit-maximizing price is exactly equal to average total cost (both short run and long run).
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           STABILIZATION POLICIES: Economic policies undertaken by governments to counteract business-cycle fluctuations and prevent high rates of unemployment and inflation. The two most common stabilization policies are fiscal and monetary. Stabilization policies are also termed countercyclical policies, meaning that they attempt to "counter" the natural ups and downs of business "cycles." Expansionary policies are appropriate to reduce unemployment during a contraction and contractionary policies are aimed at reducing inflation during an expansion. Stabilization policies are government actions, especially fiscal policy and monetary policy, designed to fix the unemployment and inflation problems created by business-cycle instability. During periods of high or rising unemployment associated with a business-cycle contraction, the appropriate action is to stimulate the economy through expansionary policies. During periods of high or rising inflation associated with a business-cycle expansion, the appropriate action is to dampen the economy through contractionary policies.Fiscal and MonetaryThe two most frequently used stabilization policies are fiscal policy and monetary policy.- Fiscal Policy: This policy makes use of government spending and/or taxes, the two components of the government's "fiscal" budget. When government increases or decreases spending, especially by changing the quantity of gross domestic product purchased, then aggregate production, employment, and national income are also affected. Government can change the amount of taxes collected from the public, as well, which then affects the amount of income available to purchase gross domestic product. This also triggers changes in aggregate production, employment, and national income.
- Monetary Policy: This policy involves the total amount of money in circulation throughout the economy, as well as interest rates in financial markets. By changing the amount of money in circulation, the public has more or less of an ability to purchase gross domestic product, which then triggers changes in overall economic activity. Money supply changes also invariably cause changes in interest rates, which subsequently affect the willingness and ability to borrow the funds used for expenditures.
Expansionary and ContractionaryStabilization policies can be either expansionary or contractionary, depending on whether the most pressing problem is excessive unemployment or excessive inflation.- Expansionary Policy: This policy is designed to stimulate the economy and to reduce unemployment by countering or preventing a business-cycle contraction. Expansionary fiscal policy is an increase in government spending and/or a decrease in taxes. Expansionary monetary policy is an increase in the money supply and/or a decrease in the interest rate.
- Contractionary Policy: This policy is designed to dampen the economy and to reduce inflation by countering or preventing the inflationary excesses of a business-cycle expansion. Contractionary fiscal policy is a decrease in government spending and/or an increase in taxes. Contractionary monetary policy is a decrease in the money supply and/or an increase in the interest rate.
A Graphical Illustration| Stabilizing the Business Cycle | 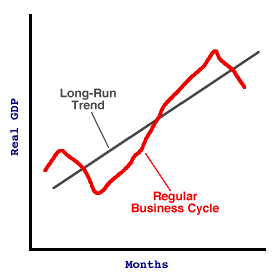 |
This graph illustrates the goal of stabilization policies. The red line is the "natural" business cycle. Rising and falling around the blue long-run trend line. But it rises and falls too much, causing inflation and unemployment. Policy makers would rather have a business cycle more like that revealed with a click of the [Stabilization Policies] button.Stabilization policies can achieve this result by countering business cycle ups and downs. When unemployment rises with a business-cycle contraction, expansionary policies are appropriate. When inflation worsens with a business-cycle expansion, contractionary policies are appropriate. Once again, note that stabilization policies are a countercyclical. Contractionary policies counter an expansion and expansionary policies counter a contraction.

Recommended Citation:STABILIZATION POLICIES, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads seeking to buy either an extra large beach blanket or a large flower pot shaped like a Greek urn. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
In his older years, Andrew Carnegie seldom carried money because he was offended by its sight and touch.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
IBEX-35
Stock Index (Spain)
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


