
|
|
CAVEAT VENDITOR: This is a latin term meaning "let the seller beware." It was developed as a counter to the buyer's warning, caveat emptor, and suggests that sellers too can be "taken to the cleaners" in a market transaction. While it's less important than caveat emptor to under appreciated consumers, it does surface from time to time.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL PHYSICAL PRODUCT: The total quantity of output produced by a firm for a given quantity of inputs. Total physical product is actually nothing more than total product. The insertion of the word "physical" merely keeps the phrase consistent with average physical product and marginal physical product, two terms useful in marginal-productivity theory and the analysis of factor demand. Total physical product is the total production of output by a firm based on the quantity of inputs used. While total physical product usually goes by the shorter name "total product," especially in short-run production analysis and market supply, the longer version "total physical product" emphasizes that production is measured in quantity units rather than monetary units.Total physical product is a cornerstone of marginal-productivity theory and the analysis of factor demand as the source for deriving marginal physical product, which is then used to calculate marginal revenue product. | Total Taco Product | 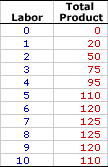 |
This table provides a few hypothetical numbers that can be used to summarize total physical product and its relation with a variable input. These numbers represent the hourly production of Shady Valley's favorite luncheon meal, Super Deluxe TexMex Gargantuan Tacos (with sour cream and jalapeno peppers). The column on the left is the variable input, specifically the number of workers employed by Waldo's TexMex Taco World, which ranges from 0 to 10. Keep in mind that these workers are not making tacos absent of other inputs. They have Waldo's TexMex Taco World restaurant and all of the capital that goes with it. However, this capital is fixed in the short run.The column on the right is the total physical product, the total number of TexMex Gargantuan Tacos produced each hour. Total physical product, Gargantuan Taco production, ranges from a low of 0 to a high of 125. Note that 125 TexMex Gargantuan Tacos is not the production for 10 workers, but the production for 7 or 8 workers. Maximum production does NOT necessarily result from maximum use of the variable input. What other sorts of observations can be made about this table? - First, total Gargantuan Taco production generally increases with the employment of extra workers, at least for the first 7 workers. This should be expected. If a firm uses more inputs, then it should get more output.
- Second, total Gargantuan Taco production does not ALWAYS increase with extra workers. Total physical product does reach a maximum of 125 Gargantuan Tacos with the employment of 7 workers, remains 125 Gargantuan Tacos with 8 workers, then falls with the addition of the 9th and 10th workers.
- Third, total Gargantuan Taco production increases a great deal for the first and second workers, but it does not increase nearly as much for the sixth and seventh workers.
Two related measures derived from total physical product are average physical product and marginal physical product.- Average Physical Product: This is the amount of output produced per worker, found by dividing the total physical product by the number of workers. If, for example, Waldo's TexMex Taco World has a staff of 5 that generates a total physical product of 110 tacos, then average physical product is 22 tacos per worker.
- Marginal Physical Product: This is the change in total physical product resulting from a change in the number of workers. Marginal physical product indicates how the total production of TexMex Gargantuan Tacos changes when an extra worker is hired or fired. For example, hiring a fifth worker means that Waldo's TexMex Taco World total physical product increases from 95 to 110 tacos. The addition of a fifth worker results in the production of an additional 15 TexMex Gargantuan Tacos.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL PHYSICAL PRODUCT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the downtown area trying to buy either shoe laces for your snow boots or a rim for your spare tire. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The wealthy industrialist, Andrew Carnegie, was once removed from a London tram because he lacked the money needed for the fare.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
SMSA
Standard Metropolitan Statistical Area
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


