
|
|
MARKETING: The ongoing process of developing, pricing, promoting, distributing, and packaging products, ideas, and services to satisfy customers’ wants and needs in a dynamic environment. Sometimes used interchangeably with sales is a misnomer. Sales, while a component of the promotion mix variable, is not the equivalent to marketing. Marketing is a broad, integrated strategy that transcends the entire organization.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           CLASSICAL AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE: An aggregate supply curve--a graphical representation of the relation between real production and the price level--that reflects the basic principles of classical economics. The classical aggregate supply curve is vertical at the full-employment level of real production indicating that the quantity of aggregate production is independent of the price level. An alternative is the Keynesian aggregate supply curve. An aggregate supply curve is a graphical representation of the relation between real production and the price level. Classical economics implies that the full-employment level of real production is maintained regardless of the price level, which creates a vertical, or perfectly elastic, aggregate supply curve. This relation results due to flexible prices, which ensure that resources markets maintain equilibrium balance at full employment. Should the price level rise or fall, wages and resource prices adjust to ensure that quantity demanded equals quantity supplied in resource markets.| Classical AS Curve | 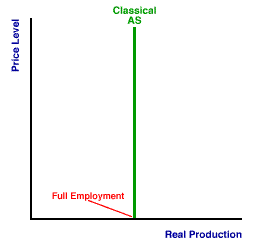 |
The exhibit to the right illustrates a classical aggregate supply (AS) curve. The obvious characteristic is that the curve is actually a vertical line. The line is vertical at the full-employment level of real production. Should the price level rise or fall, the economy moves up and down along the curve and real production remains unchanged.The full-employment level of real production corresponds to the natural unemployment rate, also termed the non-accelerating inflation unemployment rate. The measured unemployment rate is not necessarily zero. This rate includes both frictional unemployment and structural unemployment and results if the quantity of labor demanded is equal to the quantity of labor supplied. The classical aggregate supply curve looks a great deal like the long-run aggregate supply curve. Both are vertical at the full-employment level of real production. Both indicate that real production is unaffected by changes in the price level. The reason for the similarity is that the long-run aggregate supply curve is the modern embodiment of the principles of classical economics. For the classical aggregate supply curve, changes in the price level results in changes in wages and resource prices that ensure equality between quantity demanded equals quantity supplied in resource markets. For the long-run aggregate supply curve, changes in the price level results in changes in wages and resource prices that ensure equality between quantity demanded equals quantity supplied in resource markets--in the long run.

Recommended Citation:CLASSICAL AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the downtown area trying to buy either shoe laces for your snow boots or a rim for your spare tire. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Before 1933, the U.S. dime was legal as payment only in transactions of $10 or less.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
TIBOR
Tokyo Interbank Offered Rate (Japan)
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


