
|
|
OIKONOMOS: This rather strange word is a greek term meaning "household manager" or "household steward" that gave rise to the modern term economy and the whole range of related terms, including economic, economics, economist, and economize. Ironically there are those who use economics less with the goal of providing "stewardship" of the economy and more focused on the goal of extracting maximum personal gain.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           DEMAND INCREASE: An increase in the willingness and ability of buyers to purchase a good at the existing price, illustrated by a rightward shift of the demand curve. An increase in demand is caused by a change in a demand determinant and results in an increase in equilibrium quantity and an increase in equilibrium price. A demand increase is one of two demand shocks to the market. The other is a demand decrease. A demand increase results from a change in one of the demand determinants. The rightward shift of the demand curve disrupts the market equilibrium and creates a temporary shortage. The shortage is eliminated with a higher price. The comparative static analysis of the demand increase is that equilibrium quantity increases and equilibrium price increases.Demand DeterminantsAn increase in demand can result from a change in any of the five demand determinants. - Buyers' Income: An increase in buyers' income for a normal good or a decrease in buyers' income for an inferior good.
- Buyers' Preferences: An increase in buyers' preferences for the good.
- Other Prices: An increase in the price of a substitute-in-consumption or a decrease in the price of a complement-in-consumption.
- Buyers' Expectations: Expectations by buyers of an increase in the price in the future.
- Number of Buyers: An increase in the number of buyers in the market.
Old to NewFirst, consider the simple comparative static analysis of the demand increase. The diagram at the right presents the Shady Valley market for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes. The initial equilibrium price is Po and the initial equilibrium quantity is Qo. This market equilibrium, of course, persists until and unless a determinant changes, which is the nature of equilibrium. The particular change under scrutiny is an increase in demand caused by a change in any of the five demand determinants noted above. | Comparative Statics | 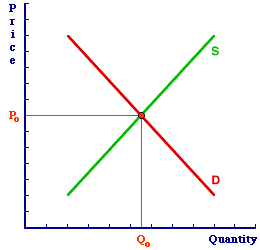 |
Suppose, for example, that buyers acquire a sudden craving for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes, which is a change in buyers' preferences. Perhaps a newly released government study proves conclusively that daily consumption of Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes increases a person's IQ by 50 points and makes that person more attractive to the opposite sex. This is just the sort of thing that is bound to increase buyers' preferences and the demand for Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes. And when demand increases, the original market equilibrium is disrupted.How is the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae market affected? A change in buyers' preferences shifts the demand curve rightward. Click the [Demand Increase] button to illustrate the rightward shift of the demand curve. The OLD market equilibrium is no longer equilibrium. A NEW market equilibrium is found at the intersection of the original supply curve and the new demand curve. Click the [New Equilibrium] button to highlight this result. The new equilibrium price is Pe and the new equilibrium quantity is Qe. Note that the price is higher and the quantity exchanged is more. Step by StepNow, consider how this demand shock to the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae market can be divided into six steps using the exhibit to the right. While the directions of the changes may differ, these six steps apply to the comparative static analysis of other demand and supply shocks. | Six Steps |  |
- First, a determinant changes. In this case, evidence that IQ is boosted and sexual attractiveness is enhanced by eating Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes induces a change in buyers' preferences. A determinant change ALWAYS starts the market adjustment process.
- Second, the determinant change causes a curve to shift. The change in preferences increases demand and causes a rightward shift of the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae demand curve. Click the [Demand Increase] button to illustrate this shift.
- Third, the shifted curve disrupts the market equilibrium, causing either a shortage or a surplus. In this example, the increase in demand creates a shortage. While buyers are now willing and able to buy more Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes, sellers continue supplying the original quantity at the original price. Up to this point, they have no reason to change. Click the [Shortage] button to highlight this imbalance.
- Fourth, the market imbalance causes the price to change. In this case, the buyers are not able to buy all of the Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes that they would like. As such, they are willing and able to buy more than is offered. So they bid up the price. Click the [Price Increase] button to illustrate this result.
- Fifth, the change in price causes changes in both quantities demanded and supplied. In this Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae market, the higher price has the intended effect of increasing the quantity supplied--which is the law of supply. It also has the unintended effect of decreasing the quantity demanded--which is the law of demand. Note that while the change in preferences induces buyers to demand more at all prices, including the original equilibrium price, the price increase causes the quantity demanded to subsequently decline.
- Sixth, changes in the quantities demanded and supplied both act to eliminate the market disequilibrium. In this example, the increase in the quantity supplied and the decrease in the quantity demanded eliminate the shortage. The price will continue to change as long as the market is out of balance with a shortage. The new equilibrium price at Pe is higher and the new equilibrium quantity at Qe is greater. Click the [New Equilibrium] button to highlight this result.
One of EightA demand increase is one of eight market disruptions--four involving a change in either demand or supply and four involving changes in both demand and supply. The other three single shift disruptions are demand decrease, supply increase, and supply decrease. The four double shifts are demand and supply increase, demand and supply decrease, demand increase and supply decrease, and demand decrease and supply increase.

Recommended Citation:DEMAND INCREASE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: June 30, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
|
It's estimated that the U.S. economy has about $20 million of counterfeit currency in circulation, less than 0.001 perecent of the total legal currency.
|

|
|
"I learned about the strength you can get from a close family life. I learned to keep going, even in bad times. I learned not to despair, even when my world was falling apart. I learned that there are no free lunches. And I learned the value of hard work. " -- Lee Iacocca
|

|
JF
Journal of Finance
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


