
|
|
BALANCED-BUDGET AMENDMENT: A proposed amendment to the U.S. Constitution that would constrain total government spending to be less than or equal to total tax collections. Such an amendment would effectively eliminate the federal deficit, which results when the spending exceeds taxes. The logic behind such an amendment is to prevent discretionary use of fiscal policy, which is often blamed for political business cycles and the resulting problems of inflation and unemployment. It is also touted as a way to limit the size of the Federal government.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           DEMAND SHOCK: A disruption of market equilibrium caused by a change in a demand determinant and a shift of the demand curve. A demand shock can take one of two forms--a demand increase or a demand decrease. This is one of two disruptions of the market. The other is a supply shock. A demand shock to the market results when the demand curve is shifted due to a change in one of the five demand determinants--buyers' income, buyers' preferences, other prices, buyers' expectations, and number of buyers.The demand shock comes in two varieties. - Increase in Demand: This is a rightward shift of the demand curve. It generates an increase in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity.
- Decrease in Demand: This is a leftward shift of the demand curve. It generates a decrease in the equilibrium price and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity.
Demand IncreaseAn increase in demand can result from a change in any of the five demand determinants. - Buyers' Income: An increase in buyers' income for a normal good or a decrease in buyers' income for an inferior good.
- Buyers' Preferences: An increase in buyers' preferences for the good.
- Buyers' Preferences: An increase in the price of a substitute-in-consumption or a decrease in the price of a complement-in-consumption.
- Buyers' Expectations: Expectations by buyers of an increase in the price in the future.
- Number of Buyers: An increase in the number of buyers in the market.
| Increase in Demand | 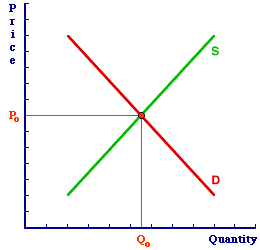 |
The comparative static analysis of an increase in demand is illustrated in the exhibit at the right. The market is disrupted when one of the five demand determinants listed above causes an increase in demand and a rightward shift of the demand curve. This can be seen by clicking the "demand increase" button. The result of this disruption, given the original equilibrium price, is a temporary shortage (click the [Shortage] button). The shortage then induces an increase in the price (click the [Price Increase] button). The price increase causes an increase in quantity supplied and a decrease in quantity demanded. The result of these quantity changes is a new equilibrium at a higher price and a larger quantity. Click the [New Equilibrium] button to display this outcome. The comparative static analysis reveals an increase in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity. An increase in demand results in an increase in the equilibrium quantity. The demand shift means that buyers want to buy more. Sellers are willing to accommodate buyers. However, to appease their increased demand, sellers must charge a higher price to cover their increasing production cost in accordance with the law of supply. Demand DecreaseAn decrease in demand can result from a change in any of the five demand determinants. - Buyers' Income: A decrease in buyers' income for a normal good or an increase in buyers' income for an inferior good.
- Buyers' Preferences: A decrease in buyers' preferences for the good.
- Buyers' Preferences: A decrease in the price of a substitute-in-consumption or an increase in the price of a complement-in-consumption.
- Buyers' Expectations: Expectations by buyers of a decrease in the price in the future.
- Number of Buyers: A decrease in the number of buyers in the market.
| Decrease in Demand |  |
The comparative static analysis of a decrease in demand is illustrated in the exhibit at the right. The market is disrupted when one of the five demand determinants listed above causes a decrease in demand and a leftward shift of the demand curve. This can be seen by clicking the [Demand Decrease] button. The result of this disruption, given the original equilibrium price, is a temporary surplus (click the [Surplus] button). The surplus then induces a decrease in the price (click the [Price Decrease] button). The price decrease causes a decrease in quantity supplied and an increase in quantity demanded. The result of these quantity changes is a new equilibrium at a lower price and a smaller quantity. Click the [New Equilibrium] button to display this outcome. The comparative static analysis reveals a decrease in the equilibrium price and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. A decrease in demand results in a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. The demand shift means that buyers want to buy less. Sellers are willing to accommodate buyers. However, to appease their decreased demand, sellers are able to charge a lower price to cover their decreasing production cost in accordance with the law of supply. Summarizing the Changes| Shift | Quantity
Change | Price
Change | | Demand Increase | Increase | Increase | | Demand Decrease | Decrease | Decrease |
Comparative static results of the two demand shocks are summarized in the table at the right. A key observation is that equilibrium quantity moves in the SAME direction as the change in demand. If demand increases, then equilibrium quantity increases. If demand decreases and quantity demanded decreases.However, because the supply curve does NOT shift, the market is constrained to move ALONG the supply curve and follow the law of supply. If the quantity increases, then the price also increases. If the quantity decreases, then so too does the price.

Recommended Citation:DEMAND SHOCK, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLACK DISMALAPOD
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing about a thrift store seeking to buy either a genuine fake plastic Tiffany lamp or a microwave over that won't burn your popcorn. Be on the lookout for small children selling products door-to-door.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
John Maynard Keynes was born the same year Karl Marx died.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
ATO
At The Opening
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


