
|
|
VARIABLE FACTOR OF PRODUCTION: An input whose quantity can be changed in the time period under consideration. This usually goes by the shorter term fixed input and should be immediately compared and contrasted with fixed factor of production, which goes by the shorter term fixed input. The most common example of a variable factor of production is labor. A variable factor of production provides the extra inputs that a firm needs to expand short-run production. In contrast, a fixed factor of production, like capital, provides the capacity constraint in production. As larger quantities of a variable factor of production, like labor, are added to a fixed factor of production like capital, the variable factor of production becomes less productive.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           CONSUMPTION EXPENDITURES DETERMINANTS: Ceteris paribus factors, other than income, that are held constant when the consumption line is constructed and which cause the consumption line to shift when they change. Some of the more important consumption expenditures determinants are interest rates, consumer confidence, wealth, and taxes. Due to the relation between consumption and saving, these determinants also cause corresponding, and opposite, shifts of the saving line. Consumption expenditures determinants are ceteris paribus factors that determine the position of the consumption line that plots the induced relation between consumption and income. Changes in these determinants then cause shifts of the consumption line. The fundamental psychological law proposed by John Maynard Keynes as an essential theoretical difference between his theory of Keynesian economics and classical economics indicates that consumption expenditures are primarily based on income. If people have more income, then they are inclined to spend more. Less income inevitably leads to less spending. However, a number of other factors also affect consumption independent of income. For example, a typical consumer like Duncan Thurly might decide to increase consumption expenditures by purchasing an excruciatingly painful root canal from his dentist, Dr. Nova Cain. This extra spending is NOT the result of a sudden windfall of income. Duncan did not receive a year-end bonus from his boss nor did he find a leather satchel of $100 bills on the sidewalk. Rather, this expenditure is undertaken for "other reasons" unrelated to his income. That specific reason is to eliminate the excruciatingly painful cavity in his tooth. Moreover, if this extra spending is not undertaken with extra income, then it necessarily results in a decline in saving. What They Do| Determinants | 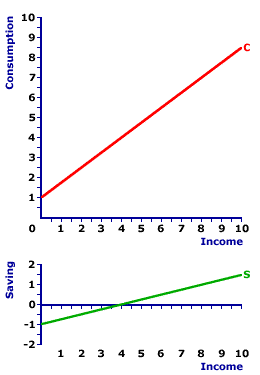
|
Consumption expenditures determinants affect the consumption line much like any determinants affect a corresponding curve--they cause the curve to shift.The exhibit to the right presents the consumption line in the top panel and the saving line in the bottom panel. The saving line is also included because consumption expenditures determinants also affect the saving line. A change in consumption expenditures are invariably matched by an opposite change in saving. Consumption expenditures determinants can trigger either an increase or a decrease in consumption and a corresponding decrease and increase in saving. (The only notable exception is taxes.) - Increase in Consumption: An increase in consumption is illustrated by an upward shift of the consumption line. At each income level, the household sector has greater consumption expenditures. However, because the greater consumption is not resulting from additional income, saving necessarily decreases. As such, the increase in consumption is matched by a decrease in saving and a downward shift of the saving line. Click the [Consumption Increase] button to illustrate.
- Decrease in Consumption: A decrease in consumption is illustrated by a downward shift of the consumption line. At each income level, the household sector has fewer consumption expenditures. Because the reduced consumption is not resulting from less income, saving necessarily increases. As such, the decrease in consumption is matched by an increase in saving and an upward shift of the saving line. Click the [Consumption Decrease] button to illustrate.
These shifts of the consumption line take center stage in Keynesian economics. They are one important source of business-cycle instability. A shift of the consumption line results in a shift of the aggregate expenditures line, which then disrupts equilibrium equality between aggregate expenditures and aggregate production.What They AreWhile individuals such as Duncan are bound to encounter a wide range of specific non-income factors affecting individual spending (including unexpected root canals), determinants affecting overall consumption expenditures by the aggregate household sector are more limited. Some of the more important determinants are:- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates discourage the borrowing used to finance some types of consumption expenditures (such as automobiles and furniture) and it increases the return on income diverted as saving into the financial markets. As such, consumption decreases and saving increases. Lower interest rates work in the opposite manner.
- Consumer Confidence: If people have more confidence about the state of the economy, they are more likely to boost their spending. However, because this extra spending is not the result of extra income, it must come from saving. As such, consumption increases and saving decreases. A drop in consumer confidence works in the opposite manner.
- Wealth: Wealth affects consumption in one of two ways. An increase in financial wealth (including stocks, bonds, and especially money) motivates the household sector to increase consumption and decrease saving. Consumption increases and saving decreases. Alternatively, an increase in physical wealth (including cars, furniture, and appliances) reduces the need to buy these goods and thus motivates the household sector to decrease consumption and increase saving.
- Taxes: Government collects taxes to pay for government activities. These taxes come from household income, specifically disposable income. An increase in taxes means a reduction in disposable income, and consequently a decrease in consumption. Because total or national income is not changing, these taxes also reduce saving. As such, unlike other determinants both consumption and saving decrease. A reduction in taxes work in the opposite direction.

Recommended Citation:CONSUMPTION EXPENDITURES DETERMINANTS, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the downtown area trying to buy either shoe laces for your snow boots or a rim for your spare tire. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Paper money used by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts prior to the U.S. Revolutionary War, which was issued against the dictates of Britain, was designed by patriot and silversmith, Paul Revere.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
ADV FRT
Advance Freight
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


