
|
|
WHEALER-LEA ACT: This was a major amendment to the Federal Trade Commission Act, passed in 1938, that gave powers to the Federal Trade Commission to investigate unfair and deceptive business practices and to prevent false advertising. The Whealer-Lea Act was a major step in moving the Federal Trade Commission into its current role as more of a consumer protection agency than a monopoly buster.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           ECONOMIC GROWTH: The long-run expansion of the economy's ability to produce output. Growth is attained by increasing the quantity or quality of the economy's resources--labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship--through such things as population growth, investment, exploration, technological innovation, and education. This is one of the five economic goals and more specifically one of the three macroeconomic goals. The other goals are full employment, stability, efficiency and equity. Economic growth is achieved by increasing the economy's ability to produce goods and services. This goal is best indicated by measuring the growth rate of production. If the economy produces more goods this year than last, then it is growing. Economic growth is also indicated by increases in the quantities of the resources--labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship--used to produce goods. With economic growth, society gets more goods that can be used to satisfy more wants and needs--people are better off; living standards rise; and scarcity is less of a problem.Graphical Indications| Production Possibilities | 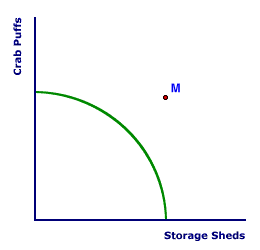 | Aggregate Market | 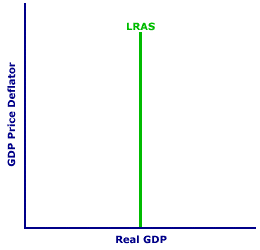
|
Economic growth is commonly illustrated by two basic graphical analyses, production possibilities model and the aggregate market model (or AS-AD analysis). Both models are presented in the exhibit to the right. The production possibilities model is in the top panel and the long-run aggregate supply curve used in the aggregate market model is in the bottom panel.- Production Possibilities: Economic growth is indicated by an outward shift of the production possibilities frontier in the top panel. To illustrate economic growth, click the [Growth] button under the production possibilities frontier. The production possibilities frontier represents the maximum output produced with available resources and current technology. If society has more resources or better technology, then it can produce more output and the frontier shifts outward.
- Aggregate Market: Economic growth is indicated by a rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve in the bottom panel. To illustrate economic growth, click the [Growth] button under the long-run aggregate supply curve. The long-run aggregate supply curve is constructed based on the assumption that flexible prices have enabled full employment of existing resources. If the quantity or quality of the resources increases, the full employment level of production also increases, leading to a rightward shift of the vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
Sources of Economic GrowthAn economy is able to achieve the goal of economic growth by increasing the quantity or quality of the resources. Consider a few of the more important examples.- Quantity of Labor: The quantity of labor increases in three basic ways: (1) natural population growth, (2) immigration from other countries, and (3) higher labor force participation rate.
- Quantity of Capital: The quantity of capital increases through the production of capital goods, which inevitably involves a tradeoff with the production of consumption goods. This tradeoff is generally termed investment.
- Quantity of Natural Resources: The quantity of natural resources that are available for production is increased through exploration. The natural resources already exist (naturally), but they can be used for production only after their existence and location is known.
- Quality of Labor: The primary means of increasing the quality of labor is through education, either formal schooling or informal on-the-job training.
- Quality of Capital: The primary means of increasing the quality of capital is through technological advances
InvestmentEconomic growth can be achieved in several different ways. However, each method involves the fundamental process of investment. Investment is the sacrifice of current benefits or rewards to pursue an activity with expectations of greater future benefits or rewards. In its simplest form investment means giving up consumption goods and producing capital goods.The quantity and quality sources of economic growth all involve investment in one way or another. Increasing the quantity of capital is an obvious example. Exploration for natural resources, such as drilling for oil, also fits most common sense notions of investment. However, increasing in the quantity of labor also reflects investment. Parents sacrifice their own consumption to raise a family. Immigrants sacrifice as they travel to a new country. The acquisition of education is also an investment, exemplified by college students who sacrifice four to five years of early adulthood for a college degree. The development of technology is also an investment with resources devoted to scientific research rather than being used for other production. The bottom line is that economic growth is achieved through investment. Without investment, there is no economic growth. The Problems of Economic GrowthThe macroeconomic goal of economic growth is generally acknowledged as a beneficial pursuit. Almost everyone gains from economic growth. Unlike other economic goals, conservatives and liberals usually agree that economic growth is good for society.However, everything has a down side and economic growth is no exception. - Lifestyle Losses: One concern with economic growth is the loss of traditional lifestyles. New products, new technologies, faster transportation, and other changes that accompany economic growth also tend to disrupt traditional ways of living. For example, families might find themselves scattered across the country.
- Generational Transfers: Another concern with economic growth is the transfer of income and wealth from one generation to the next. One generation makes the investment in capital, technology, or education, but the next generation then reaps the reward of this growth. One example is public education for the young financed by taxes on the elderly. Some question whether or not it is fair for some, like the elderly, to sacrifice with no prospects of personally benefitting from the investment.
- Disamenities: A third problem with economic growth is an increase in disamenities, such as pollution, congestion, and natural resource depletion. In that economic growth means more production of "goods", it also means the generation of more "bads." The automobile, for example, improves travel but causes air pollution.

Recommended Citation:ECONOMIC GROWTH, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads seeking to buy either an extra large beach blanket or a large flower pot shaped like a Greek urn. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Potato chips were invented in 1853 by a irritated chef repeatedly seeking to appease the hard to please Cornelius Vanderbilt who demanded french fried potatoes that were thinner and crisper than normal.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
IIP
Index of Industrial Production
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


