
|
|
GENERAL AGREEMENT ON TARIFFS AND TRADE: A treaty, signed in 1947 by 23 countries including the United States, that was designed to reduce trade barriers. It now carries the signatures of about 100 countries and over the years has been pretty darn effective in reducing tariffs, eliminating some import quotas, and promoting commerce.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARGINAL FACTOR COST CURVE, MONOPSONY: A curve that graphically represents the relation between marginal factor cost incurred by a monopsony for hiring an input and the quantity of input employed. A profit-maximizing monopsony hires the quantity of input found at the intersection of the marginal factor cost curve and marginal revenue product curve. The marginal factor cost curve for a monopsony with market control is positively sloped and lies above the average factor cost curve. Monopsony is a market structure with a single buyer or in terms of factor markets, a single employer. This means that monopsony is a price maker with control over the buying side of the market. Market control means monopsony faces a positively-sloped supply curve. To buy a larger quantity, it must pay a higher price.The marginal factor cost curve reflects the degree of market control held by a firm. For a perfectly competitive firm with no market control, the marginal factor cost curve is a horizontal line. For firms with more market control, especially monopsony, the marginal factor cost curve is positively sloped and lies above the average factor cost curve. Marginal Factor Cost Curve,
Monopsony | 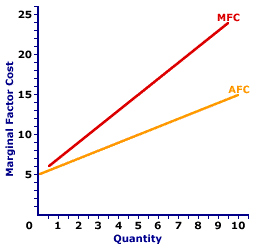 |
The marginal factor cost curve (MFC) for OmniKing Island Resort is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that OmniKing is a monopsony buyer of workers and thus faces a positively-sloped supply curve. Larger quantities of input can be had only with higher prices.The vertical axis measures marginal factor cost and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of input (workers). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 workers, it could go higher. This curve indicates that if OmniKing hires the first worker, then marginal factor cost is $6. Alternatively, if it hires the tenth worker, then marginal factor cost is $24. For reference, the factor supply curve (and average factor cost curve, AFC) is also presented in the exhibit. The key observation is that the positively-sloped marginal factor cost curve (MFC) lies above the supply curve (AFC) facing OmniKing for hiring labor. The positioning of the marginal factor cost curve above the average factor cost curve reflects the mathematical relation between an average and a marginal. Although this marginal factor cost curve is based on the employment activity of OmniKing Island Resort, a well-known monopsony firm, it works for any buyer with market control. Monopsonistic competition and oligopsony firms that also face positively-sloped supply curves generate comparable marginal factor cost curves.

Recommended Citation:MARGINAL FACTOR COST CURVE, MONOPSONY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: June 30, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GREEN LOGIGUIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a crowded estate auction trying to buy either hand lotion, a big bottle of hand lotion or a lighted magnifying glass. Be on the lookout for gnomes hiding in cypress trees.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
It's estimated that the U.S. economy has about $20 million of counterfeit currency in circulation, less than 0.001 perecent of the total legal currency.
|

|
|
"I learned about the strength you can get from a close family life. I learned to keep going, even in bad times. I learned not to despair, even when my world was falling apart. I learned that there are no free lunches. And I learned the value of hard work. " -- Lee Iacocca
|

|
SPSS
Statistical Product and Service Solutions, Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (software)
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


