
|
|
AGGREGATE EXPENDITURE LINE: A line representing the relation between aggregate expenditures and gross domestic product used in the Keynesian cross. The aggregate expenditure line is obtained by adding investment expenditures, government purchases, and net exports to the consumption line. As such, the slope of the aggregate expenditure line is largely based on the slope of the consumption line (which is the marginal propensity to consume), with adjustments coming from the marginal propensity to invest, the marginal propensity for government purchases, and the marginal propensity to import. The intersection of the aggregate expenditures line and the 45-degree line identifies the equilibrium level of output in the Keynesian cross.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL FACTOR COST CURVE, PERFECT COMPETITION: A curve that graphically represents the relation between total factor cost incurred by a perfectly competitive firm when using a given factor of production to produce a good or service. The total factor cost curve is most important in factor market analysis for the derivation of the marginal factor cost curve. Perfect competition is a market structure with a large number of small participants (buyers and sellers). The good exchanged in the market is identical, regardless of who sells or who buys. Participants have perfect knowledge and perfect mobility into and out of the market. These conditions mean perfectly competitive buyers are price takers, they have no market control and must pay the going market price for all inputs bought.The total factor cost curve reflects the degree of market control held by a firm. For a perfectly competitive firm with no market control hiring inputs under perfect competition, the total factor cost curve is a straight line that emerges from the origin. For firms with market control, including monopsony, oligopsony, or monopsonistic competition, the total factor cost curve increases at an increasing rate. The shape of the total factor cost curve thus indicates the degree of market control possessed by the factor buyer. Total Factor Cost Curve,
Perfect Competition | 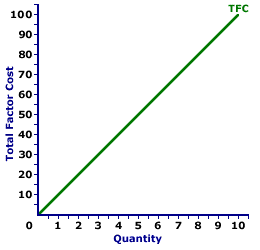 |
Total factor cost is commonly represented by a total factor cost curve, such as the one displayed in the exhibit to the right. This particular total factor cost curve is that for labor hired by a hypothetical buyer, Maggie's Macrame Shoppe. Maggie's Macrame Shoppe is one of thousands of small retail stores in the greater Shady Valley metropolitan area that hires labor with identical skills. As such, Maggie pays the going wage for labor.The vertical axis measures total factor cost and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of input (workers). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 workers, the nature of perfect competition indicates it could go higher. This curve indicates that if Maggie hires 1 worker, then she pays $10 of total factor cost. Alternatively, if she hires 10 workers, then she pays $100 of total factor cost. Should she hire 100 workers, then she would move well beyond the graph, with $1000 of total factor cost. The "curve" is actually a "straight line" because Maggie is a price taker in the labor market. She pays $10 for each worker whether she hires 1 worker or 10 workers. The constant price is what makes Maggie's total factor cost curve a straight line, and which indicates that Maggie has no market control.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL FACTOR COST CURVE, PERFECT COMPETITION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
YELLOW CHIPPEROON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads trying to buy either a T-shirt commemorating the 2000 Olympics or a genuine fake plastic Tiffany lamp. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from former employers.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
More money is spent on gardening than on any other hobby.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
BNA
Bureau of National Affairs
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


