
|
|
NEGATIVE RELATION: A relation, either a principle or hypothesis, in which an increase one variable is associated with a decrease in the other variable. A negative, or indirect, relation is most commonly illustrated by a downward sloping line. It can also be represented by an equation in which the slope value is negative.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARGINAL UTILITY CURVE: A curve illustrating the relation between the marginal utility obtained from consuming an additional unit of good and the quantity of the good consumed. The negative slope of the marginal utility curve reflects the law of diminishing marginal utility. The marginal utility curve also can be used to derived the demand curve. | Roller Coaster Utility | 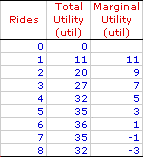 |
The marginal utility curve is an essential component of consumer demand theory and utility analysis. It graphically captures the relation between the utility generated from the consumption of an additional unit of a good and the quantity of the good consumed. This relation provides a basis for understanding market demand and the law of demand.To set the stage for the marginal utility curve, consider the table presented here. This table reports the total utility and marginal utility generated when Edgar Millbottom, Shady Valley's resident roller coaster aficionado, spends the day riding the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster at the local Shady Valley Amusement Park. Edgar takes 8 separate rides on the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster, graciously recording the total utility he accumulates after each ride. The task at hand is to plot the marginal utility values from the table into a graph. The graph below is ideally suited for the construction of the marginal utility curve for Edgar's 8 rides on the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster. | Deriving the Curve |  |
First, a few words about the existing graph. - The joined axes at the right present the plotting area.
- The horizontal axis measures quantity, the number of rides on the roller coaster. This ranges from 0 to 8.
- The vertical axis measures marginal utility, in utils, ranging from 0 to 12.
The next step is relatively easy. Click the [Plot] button to plot points indicating the marginal utility associated with each ride on the roller coaster. - For the first ride, marginal utility is 11 utils.
- For the second rides, marginal utility is 9 utils.
- For the third ride, marginal utility is 7 utils.
- And on it goes...
Note that each point is plotted halfway between the previous quantity and the subsequent quantity. This method is used because marginal utility represents a change from one quantity to another.If the quantity consumed is continuously divisible, rather than coming in discrete amounts, then these eight points represent eight of an infinite number that capture the relation between marginal utility and quantity. To illustrate the other possible points, click the [Curve] button. The resulting line is the marginal utility curve. Consider these three observations about the curve. The marginal utility curve is negatively sloped. It decreases as the number of rides increases. Each additional ride adds less utility that the preceding one.
The marginal utility curve begins in the positive range of values, eventually intersects the horizontal axis, then enters the negative range. The quantity at which the marginal utility curve intersects the horizontal axis (6 rides) of zero marginal utility corresponds with the maximum value of total utility.
The negative slope of this marginal utility curve is due to the law of diminishing marginal utility. In that marginal utility plays a primary role in the price buyers are willing and able to pay for good, this provides insight into the negative slope of the demand curve.

Recommended Citation:MARGINAL UTILITY CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BROWN PRAGMATOX
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing through a long list of dot com websites seeking to buy either a case of blank recordable DVDs or a pair of red goulashes with shiny buckles. Be on the lookout for mail order catalogs with hidden messages.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
It's estimated that the U.S. economy has about $20 million of counterfeit currency in circulation, less than 0.001 perecent of the total legal currency.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
MRP
Marginal Revenue Product
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


