Market share is the portion of total activity in an industry attributable to one or more firms. Market share provides insight into market structure. For example, a firm with a market share of 100 percent is a monopoly. It has 100 percent of the market. A firm with a market share of 0.001 percent is most likely an indication of monopolistic competition. It is one of 100,000 firms in the market.In contrast, a firm with a market share of 10 percent, 25 percent, or 50 percent, is oligopolistic. Such a firm is one of only a handful of firms. In fact, calculating market share is really only meaningful for oligopolistic firms.
Soft Drink Market Shares
| Soft Drink Sales | 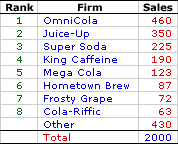 |
For further insight in to the market share concept, consider the hypothetical oligopolistic Shady Valley market for soft drinks. This market contains a handful of competitors, including OmniCola (a wholely-owned subsidiary of OmniConglomerate, Inc.), Juice-Up, and Super Soda. A list of the major players and their total annual sales is presented in the exhibit to the right.Total industry sales come in about $2,000 million. The leader of the industry is OmniCola with $460 million in sales. Number two on the list is Juice-Up with $350 million in sales. And third place goes to Super Soda with sales coming in at $225 million.
The market share for each firm is calculated as that portion of the total market sales accounted for the firm. OmniCola, for example, has 23 percent of the total market (= $460/$2000). Juice-Up has a market share of 17.5 percent (= $350/$2000). And Super Soda comes in with a market share of 11.25 percent (= $225/$2000). Market shares for each of the other firms listed in the table are calculated in the same way.
From these market share numbers, it is easy to see than OmniCola is the dominant firm in the Shady Valley soft drink market. While OmniCola does not totally dominate the market, the other firms undoubtedly look to OmniCola as the firm to beat. They are likely to develop advertising strategies, new product innovations, and perhaps even prices designed to acquire a portion of OmniCola's market share. In fact, Juice-Up, Super Soda, and one or two of the others might even consider merging to form a more formidable competitor for OmniCola.
Concentration Ratios
While market shares provide insight in their raw forms, they provide extra meaning when used to calculate concentration ratios. Concentration ratios measure the proportion of total activity in an industry attributable to a given number of the largest firms in the industry. The two most common concentration ratios are for the four largest firms and the eight largest firms. The four-firm concentration ratio is the proportion of total activity attributable by the four largest firms in the industry and the eight-firm concentration ratio is proportion of total activity attributable by the eight largest firms in the industry.In essence, concentration ratios are calculated by summing the market shares of the four or eight largest firms in an industry.
The four-firm concentration ratio for the Shady Valley soft drink is the sum of the market shares for OmniCola (23 percent), Juice-Up (17.5 percent), Super Soda (11.25 percent), and King Caffeine (9.5 percent), which is 61.25 percent. This number means that the four largest firms in the market account for 61.25 percent of total sales.
The eight-firm concentration ratio is calculated in a similar manner. The top four firms listed above, plus the next four firms, account for 78.5 percent of total sales in the Shady Valley soft drink market.
Herfindahl Index
Market shares are also used to calculate a slightly more sophisticated measure of concentration--the Herfindahl index. This index is calculated as the sum of the squares of market shares for every firm in the industry. This index provides a different way of looking at an oligopolistic market. First, in includes information about every firm in the industry (rather than just the four or eight largest firms). Second, by squaring the market shares, it gives extra importance to the largest firms (based on the presumption that market control is not merely proportion to market share).
The Herfindahl index for the Shady Valley soft drink market is the sum of the square of OmniCola's market share (23-squared equals 529), Juice-Up's market share (17.5-squared equals 306.25), Super Soda's market share (11.25-squared equals 126.563), plus every other firm in the market.
The resulting Herfindahl index is 1177.003. While this number is not as intuitive as the concentration ratio, an index below 1,000 is generally viewed has having low concentration, while one over 2,000 is viewed as having high concentration. This number of the Shady Valley soft drink market is thus considered medium concentration.
MARKET SHARE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].


