
|
|
ADJUSTMENT, SHORT-RUN AGGREGATE MARKET: Disequilibrium in the short-run aggregate market induces changes in the price level that restore equilibrium. If the price level is above the short-run equilibrium price level, economy-wide product market surpluses cause the price level to fall. If the price level is below the short-run equilibrium price level, economy-wide product market shortages cause the price level to rise. In both cases short-run equilibrium is restored. You might want to compare adjustment, long-run aggregate market. Price level changes induce changes in both aggregate expenditures and real production. Unlike the long-run aggregate market, changes in the price level can induce changes in short-run aggregate supply, making it greater or less than full-employment real production.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           NET-EXPORT EFFECT: A change in aggregate expenditures on real production, especially net exports from the foreign sector, that results because a change in the price level alters the relative prices of exports and imports. The net-export effect, also termed the international-substitution effect, is one of three effects underlying the negative slope of the aggregate demand curve associated with a movement along the aggregate demand curve and a change in aggregate expenditures. The other two are real-balance effect and interest-rate effect. The net-export effect is somewhat analogous to the substitution effect underlying the negative slope of the market demand curve. The net-export effect is one of three basic effects that indicate why aggregate expenditures are inversely related to the price level. The net-export effect works like this: A higher price level increases the relative price of domestic exports to other countries while decreasing the relative price of foreign imports from other countries. This results in a decrease in exports and an increase in imports and thus a decrease in net exports. A lower price level has the opposite affect, causing a decrease in the relative price of domestic exports to other countries while increasing the relative price of foreign imports from other countries. This results in an increase in exports and a decrease in imports and thus an increase in net exports. | Along the Curve | 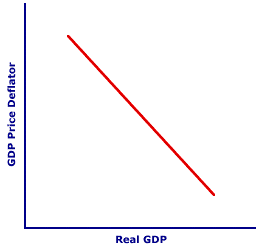 |
Before examining the details of the net-export effect, consider the specifics of what it does. A typical aggregate demand curve is presented in the exhibit to the right. The negative slope of the aggregate demand curve captures the inverse relation between the price level and aggregate expenditures on real production.When the price level changes, the net-export effect is activated, which is what then results in a change in aggregate expenditures and a movement long the aggregate demand curve. To illustrate this process, click the [Change Price Level] button. Aggregate demand is the demand for domestic production--goods and services produced by the domestic economy. A change in the price level is a change in the price of this domestic production. Other countries in the foreign sector produce goods and services, too. If the price level increases in one country, then the production in other countries becomes relatively cheaper. If the domestic price level increases, then buyers in other countries (the foreign sector) are discouraged from buying as many exports from the domestic economy, switching instead to their own production or maybe exports from another country. In addition, domestic buyers (including the household, business, and government sectors) are motivated to switch from the now more expensive domestic production to the now relatively cheaper foreign imports. This comparison of prices among different countries gives rise to the net-export effect. In particular, an increase in the price level increases imports and decreases exports, which results in a decrease in net exports. A decrease in the price level has the opposite effect on imports, exports, and net exports. Suppose, for example, that Duncan Thurly has a daily craving for cheese that is satisfied by purchasing good ol' American-made cheese produced in the American state of Wisconsin. This daily purchase is, of course, an expenditure on domestic production. How might Duncan react if the domestic economy's price level increases, and with it the price of Wisconsin cheese? He might satisfy his cheese-craving with the imported variety, probably Swiss cheese from Switzerland. If so, then his expenditures on domestic production (Wisconsin cheese) falls as his purchase of foreign production (Swiss cheese) increases. The end result is that Duncan has become a living, breathing, cheese-eating application of the net-export effect.

Recommended Citation:NET-EXPORT EFFECT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 1, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
RED AGGRESSERINE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time flipping through mail order catalogs wanting to buy either a how-to book on wine tasting or a bookshelf that will fit in your closet. Be on the lookout for slow moving vehicles with darkened windows.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The wealthy industrialist, Andrew Carnegie, was once removed from a London tram because he lacked the money needed for the fare.
|

|
|
"Experience keeps a dear school, but fools will learn in no other. " -- Benjamin Franklin
|

|
LBO
Leveraged Buyout
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


