
|
|
YIELD CURVE: A curve plotting the yields (or returns) on securities with different maturity lengths. The standard yield is for U.S. Treasury securities with lengths ranging from 90 days to 30 years. The five maturity lengths are usually 90 day, 180 day, 2 year, 5 year, 10 year, and 30 year. The shape and slope fo the yield curve indicates the state of the economy and what's likely to come. A normal yield curve has a slight positive slope, with slightly higher yields for longer maturity securities. A steep yield curve suggests the end of a contraction and beginning of an expansion. An inverted, or negatively sloped yield curve is the sign of an upcoming contraction.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           CONSTRAINED UTILITY MAXIMIZATION: The process of obtaining the highest possible level of utility from the consumption of goods or services, under given restrictions, when the highest overall level of utility cannot be reached. The notion of constrained utility maximization is a modification of the more general utility maximization assumption. It is based on the recognition that consumers might be restricted from achieving the absolute maximum level of utility. The primary restrictions tend to be the amount of income available relative to price paid. Constrained utility maximization generally does reach the peak of the total utility curve. While the generic notion of utility maximization as the unrestricted pursuit of utility is important to the study of economics and consumer demand theory, everyday life is primarily guided by the notion of constrained utility maximization. People seldom maximize utility outright. They must do the best they can under assorted constraints and restrictions.Utility Analysis| Roller Coaster Utility | 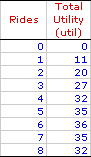 |
The accompanying table can be used to illustrate constrained utility maximization. The numbers indicate the total utility obtained by Edgar Millbottom while riding the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster at the Shady Valley Amusement Park. The right-hand column indicates the accumulated satisfaction Edgar receives from riding the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster 8 times during his day at the amusement park.While unrestricted utility maximization would see Edgar ride the roller coaster 6 times and receive 36 utils of satisfaction, assorted constraints might prevent him from doing so. Consider a few examples: - Maybe the lines are so long that he can squeeze in ONLY 4 rides during his day at the amusement park.
- Maybe several of his closest friends lock him in one of the restroom stalls for several hours, thus preventing him from even reaching the roller coaster.
- Maybe an earthquake shakes the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster into a pile of splintered rumble after his second ride.
- Or more relevant to the study of demand, maybe the amusement park charges a $1 per ride and Edgar has only $4 dollars to spend.
For the last example, the best that Edgar can do is 4 trips around the coaster track. His constrained utility maximization is only at 32 utils rather than 36 utils. Income and prices inevitably impose constraints on the utility generated from consumption.Indifference Curve Analysis| Two Goods | 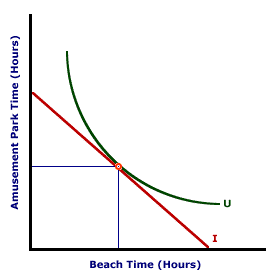 |
Constrained utility maximization can be incorporated quite easily in standard utility analysis. However, it is even more important to indifference curve analysis.The standard diagram used for indifference curve analysis is presented in the exhibit to the right. The indifference curve, labeled U, presents all combinations of two goods that provide the same amount of utility. The income or budget constraint, labeled I, shows the alternative combinations of the two goods that the buyer can purchase given a specific amount of income and existing prices. In this analysis, the consumer maximizes utility by reaching the indifference curve corresponding to the highest possible level of utility, given the existence of the budget constraint. This is achieved at a point of tangency, that is, where the budget constraint just touches the indifference curve a single point.

Recommended Citation:CONSTRAINED UTILITY MAXIMIZATION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BROWN PRAGMATOX
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing through a long list of dot com websites seeking to buy either a case of blank recordable DVDs or a pair of red goulashes with shiny buckles. Be on the lookout for mail order catalogs with hidden messages.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The penny is the only coin minted by the U.S. government in which the "face" on the head looks to the right. All others face left.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
BLS
Bureau of Labor Statistics
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


