
|
|
BANK ASSETS: What a bank owns, including loans, reserves, investment securities, and physical assets. Bank assets are typically listed on the left-hand side of a bank's balance sheet. Bank liabilities, what a bank owes, are listed on the right-hand side of a bank's balance sheet. Net worth is the difference between assets and liabilities. The largest asset category of most bank is loans, which generates interest revenue. A critical asset category used to maintain the safety of deposits is reserves (vault cash and Federal Reserve deposits).
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           EQUILIBRIUM QUANTITY: The quantity that exists when a market is in equilibrium. Equilibrium quantity is simultaneously equal to both the quantity demanded and quantity supplied. In a market graph, the equilibrium quantity is found at the intersection of the demand curve and the supply curve. Equilibrium quantity is one of two equilibrium variables. The other is equilibrium price. Equilibrium quantity is the quantity exchanged when a market is in balance. Because quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal, there is no shortage nor surplus in the market, which means that neither buyers nor sellers are inclined to change the price or the quantity, which is an essential condition for equilibrium.The MarketThe market model',500,400)">model displayed in the exhibit here can be used to identify the equilibrium quantity. This particular model represents the market for 8-track tapes, which are filled with the works of classic performers such as The Carpenters and Englebert Humperdink. The buyers and sellers happen to be folks attending the 88th Annual Trackmania 8-Track Tape Collectors Convention at the Shady Valley Exposition Center.| Equilibrium Quantity | 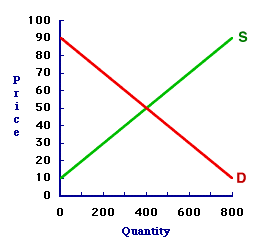
|
Before getting to the equilibrium quantity consider the market itself. - First, the demand curve (D) is negatively sloped--higher prices correspond with smaller quantities. This negative slope indicates the law of demand.
- Second, the supply curve (S) is positively sloped--higher prices correspond with large quantities. This positive slope indicates the law of supply.
Clearing the MarketEquilibrium quantity results when the market is in balance, which is equality between quantity demanded and quantity supplied. The market is clear of any shortage or surplus. The only quantity that accomplishes this task is at the intersection of the demand curve and supply curve. This intersection point, and the quantity that results, can be identified by clicking the [Equilibrium Quantity] button in the exhibit.Doing so reveals that the equilibrium quantity is 400 tapes. At this quantity, the demand curve and supply curve intersect. The quantity demanded is 400 tapes and the quantity supplied is 400 tapes. The quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. The buyers can buy all that they want, so there is no shortage. The sellers can sell all that they want, so there is no surplus. Neither buyers nor sellers are motivated to change the price. The forces of demand and supply are in balance. This is the ONLY quantity that has a balance between these two quantities. Best of all, because this is equilibrium, the equilibrium quantity of 400 tapes does not change and the equilibrium price of 50 cents does not change unless or until an external force intervenes.

Recommended Citation:EQUILIBRIUM QUANTITY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 5, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
|
On a typical day, the United States Mint produces over $1 million worth of dimes.
|

|
|
"Plans are only good intentions unless they immediately degenerate into hard work." -- Peter Drucker, management consultant
|

|
SRO
Self-regulatory Organizations
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


